Database Reference
In-Depth Information
Delayed Durability
In the previous chapter, we looked at memory-optimized tables, what you need to
do to create them, and how they can help improve performance. In this chapter, we
will have a look at another new feature in SQL Server 2014 that can also improve
database performance, a feature called
Delayed Durability
. This makes use of an in-
memory transaction log feature, which delays writing transaction log entries to disk.
Database theory suggests that relational database management systems and their
transactions should be atomic, consistent, independent, and durable; often referred
to as
ACID
. SQL Server makes transactions durable by writing transactions to its
transaction log. If you suffer a bottleneck after writing a transaction to the log, your
system can suffer from poor performance. SQL Server 2014 introduces the concept of
Delayed Durability, which offers you (the database administrator) some control on
how SQL Server writes transactions to the transaction log. However, be aware that if
you change this setting, there is the possibility of losing some data in the event of a
system crash or failure.
In this chapter, you will learn about:
• Full transaction durability
• Delayed transaction durability
• Full versus Delayed
• When should you use delayed transaction durability
• Delayed Durability and potential data loss
• Delayed Durability and other SQL Server features
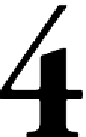
Search WWH ::

Custom Search