Java Reference
In-Depth Information
Salary e1 = new Salary(“Salary1”, “Palo Alto, CA”,
1, 100000.00);
Hourly e2 = new Hourly(“Hourly2”, “Cupertino, CA”, 2, 100.00);
Contractor e3 = new Contractor(“Contractor3”, “Milpitas, CA”,
3, 1000.00);
myCompany.put(new Integer(e1.hashcode()), e1);
myCompany.put(new Integer(e2.hashcode()), e2);
myCompany.put(new Integer(e3.hashcode()), e3);
System.out.println(“The size of the hash table is “
+ myCompany.size());
int size = myCompany.size();
for(int i = 1; i <= size; i++)
{
Employee current =
(Employee) myCompany.get(new Integer(i));
if(current instanceof Hourly)
{
((Hourly) current).setHoursWorked(40);
}
else if(current instanceof Contractor)
{
((Contractor) current).setDaysWorked(5);
}
current.computePay();
current.mailCheck();
}
myCompany.remove(new Integer(2));
System.out.println(“The size is now “ + myCompany.size());
}
}
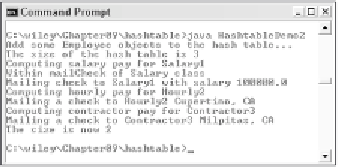
Figure 9.11
Output of the HashtableDemo2 program.