Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
c
d
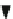
Fig. 4.14 State-of-the-art structures (a), (b), and (c) proposed in [
47
], and (d) proposed in [
48
-
50
]
In [
48
-
51
], an approach at the coding unit level is proposed, with several similar
methods based on the prediction of a DV for the current coding view by interpo-
lation of DVs from neighboring views.
4.3.2 Proposition for a New Inter-view Reference
Pictures Configuration
4.3.2.1 Reference and Proposed Scheme
In [
52
] we propose the
Central2D
scheme illustrated in Fig.
4.15b
. This two
dimensional inter-view reference picture structure exploits the two dimensional
view alignment.
Central2D
can be applied to an
N
M
views configuration. The
central view is encoded first without inter-view references. Then the
N
1 (and
respectively
M
1) views in the same horizontal (and resp. vertical) axis as the
central view are encoded with only one inter-view reference (which is the nearest
view in the central direction). Finally, the remaining views are encoded using one
horizontal and one vertical inter-view references (which are the nearest views in the
central direction). It enables the use of a horizontal and a vertical inter-view
reference picture for a large number of views (only
M
1 views do not have
horizontal and vertical reference pictures). This method minimizes the distance
between the coding views and their inter-view reference pictures because it uses the
closest neighbor and does not use diagonal references.
þ
N