Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
Locaon Dependent Interacon
(a=3)
0,3
0,25
0,2
Scenario 1
Scenario 2
Scenario 3
Scenario 4
Scenario 5
0,15
0,1
0,05
0
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Users
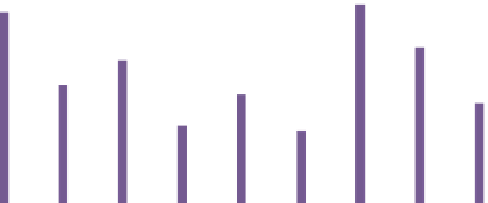
Fig. 12.9 Location dependent interaction (
ʱ¼
3)
especially in scenarios 4 and 5 that put more emphasis on the video conference
interactions.
In Fig.
12.8
, we have applied
ʱ¼
1, thus the location connectivity variation
behaviour is taken into account but with limited importance. Location dependent
interaction probabilities for user 9 and user 10 remain high, especially in scenarios
4 and 5, but also user 5 is considered, as the interaction model is not very good, but
s/he is very stable with respect to the connectivity probability.
Finally, in Fig.
12.9
, we have applied
3, thus the location connectivity
variation behaviour is seriously taken into account. Location dependent interaction
probabilities for user 9 and user 10 are now much lower, while user 5 has an
increased location dependent interaction probability as s/he is very stable as far as
the connectivity probability.
In general, we believe that
ʱ¼
3 is closer to the value that needs to be selected,
as we consider the location connectivity variation quite important for the network
overlay nodes selection.
ʱ¼
Conclusions
Tele-immersive 3D communications pose significant importance in the net-
work delivery. We have investigated the benefits from network awareness for
the provision of networked content delivery and optimization of the network
overlays. While there are multiple benefits, in the context of Tele-immersive
3D communications, we may highlight the following:
(a) The awareness of network topology and of its characteristics can guide
content providers to tailor the quality of the content offered to the end
users.
(b) The infrastructure provider can better utilize auxiliary resources, includ-
ing the activation and operation of replication servers (caches).