Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
through the eye-glasses, this value corresponded to about 7.5 cm/m
2
and thus to
15 % of the screen
s peak brightness as specified by ITU-R BT.500 [
36
].
'
10.3.2.4 Stimuli
The stereoscopic sequences consisted of a left-view and a right-view image which
were generated by the MATLAB psychtoolbox [
37
,
38
]. Each image contained a
foreground object and a static background. A black Maltese cross which was
frequently used in such kind of psychometric experiments [
39
,
40
] was used as
the foreground object with a resolution of 440
440 pixels corresponding to a
visual angle of 7.6
. As it contained both high and low spatial frequency compo-
nents, it was supposed to limit the influence of one particular spatial frequency in
the experiment [
41
].
The background was generated by adding salt and pepper noise to a black image
of Full HD resolution, and then filtered by a circular averaging filter with radius of
5. The reason for using this kind of image as the common background of all stimuli
was that it could preclude all of the monocular cues on stereopsis.
For the planar motion stimuli, the trajectory of the moving object is a circle with
center point at the center of the screen, and radius of 300 pixels, approximately 10
of visual angle. The motion direction of the object was anti-clockwise. An example
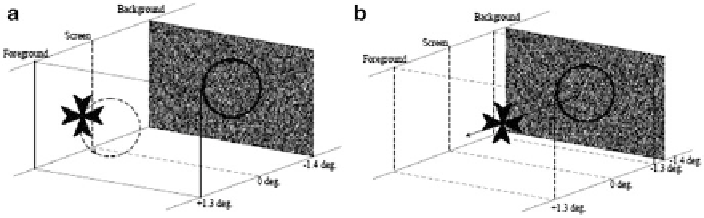
of the stimuli is shown in Fig.
10.5a
, in which the foreground object is placed in
front of the screen with an angular disparity of 1.3
. For the static stimuli, the
Maltese cross was positioned at the center of the screen. For the in-depth motion
stimuli, the Maltese cross was positioned in the center of the screen and moved back
and forth to the viewers. An example is shown in Fig.
10.5b
, in which the
foreground object is moving in the depth plane with disparity amplitude of 2.6
and offset of 0
.
Fig. 10.5 (a) An example of stimulus with planar motion in the experiment. The foreground
object is moving at the depth plane with a disparity of 1.3
. The background is placed at a fixed
depth plane of
1.4
. The motion direction of the Maltese cross is anti-clockwise. (b) An example
of stimulus with in-depth motion in the experiment. The disparity amplitude of the Maltese cross is
2.6
, and offset is 0
. The foreground object is moving in depth between disparities +1.3 and
1.3
back and forth