Database Reference
In-Depth Information
3.2
The Oracle Instance
The Oracle instance is the part of an Oracle installation executing in mem-
ory when the database is mounted, running, and available for use. That
mounted and running database consists of memory structures or buffers
and several processes.
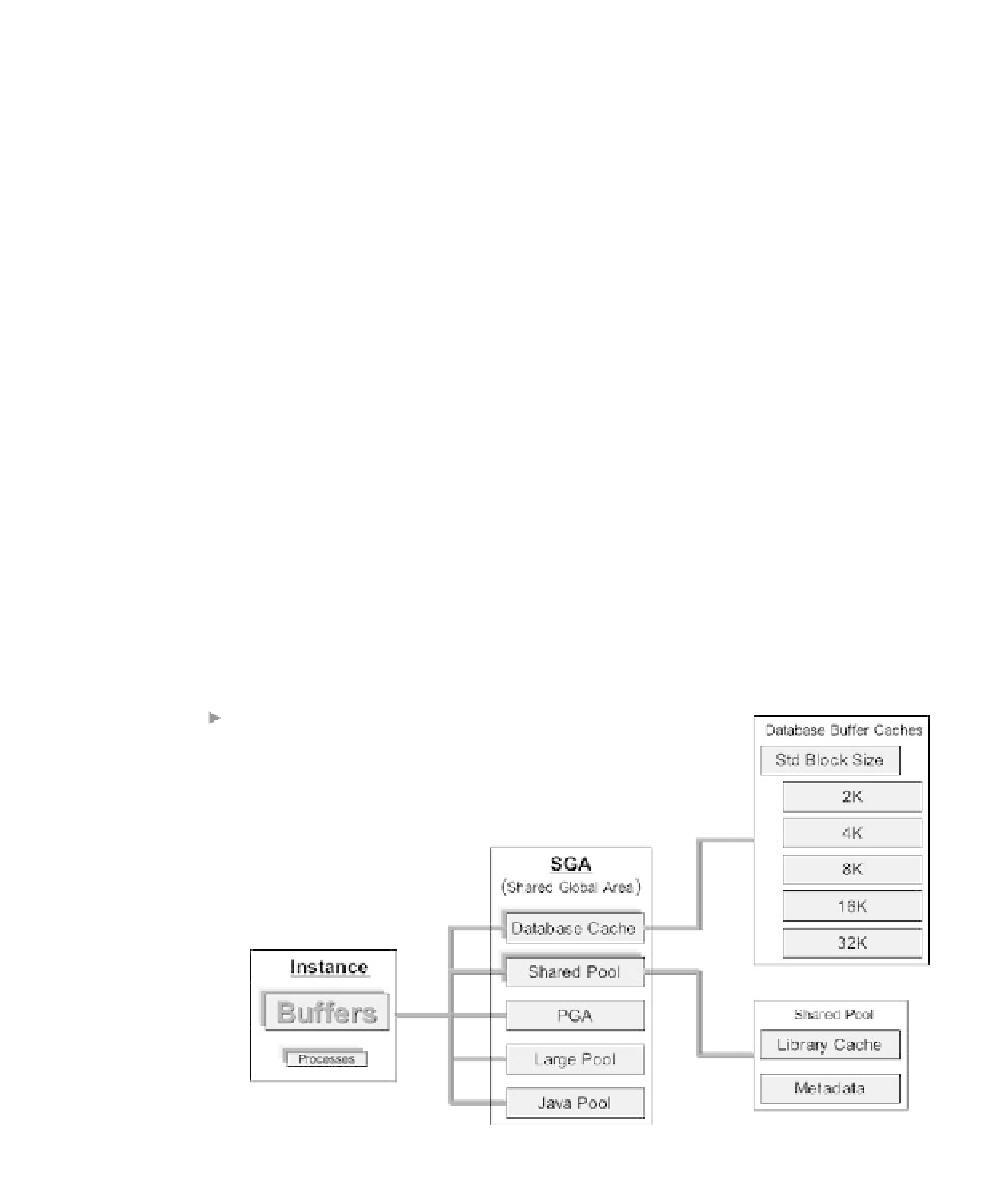
Memory structures are shown in Figure 3.6.
Much of the memory structure or buffers is known collectively as
the Shared Global Area (SGA). The SGA contains database buffer
caches, the shared pool, and the redo log buffer.
Somewhat more loosely connected are the large pool, the java
pool, and connection session memory or program global area
(PGA).
Processes:
Nonbackground or foreground processes are shown in Figure 3.7
and include network connectivity and client connection service
processing. These processes include listeners, agents, shared and
dedicated server processes, plus dispatcher processes. Although the
listener and agent processes are not part of an Oracle instance,
they execute on the database server.
Figure 3.6
Oracle Instance
Memory Buffers.