Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
wouldtakesome time to migrate fromkeyword queries to factqueries. Therefore, we
selectedavery conservative ratioof50/50 fact-to-keyword query types with a view
to adding more hardware if needed. After automatically generating millionsofquery
files, we heavily loadedthesystemwiththe queries tosimulate heavy tra
c using
JMeter, amulti-threaded client webuser simulation applicationfromthe Apache
Jakarta organization. Based onthese simulations, we deployedwithonlyfour nodes.
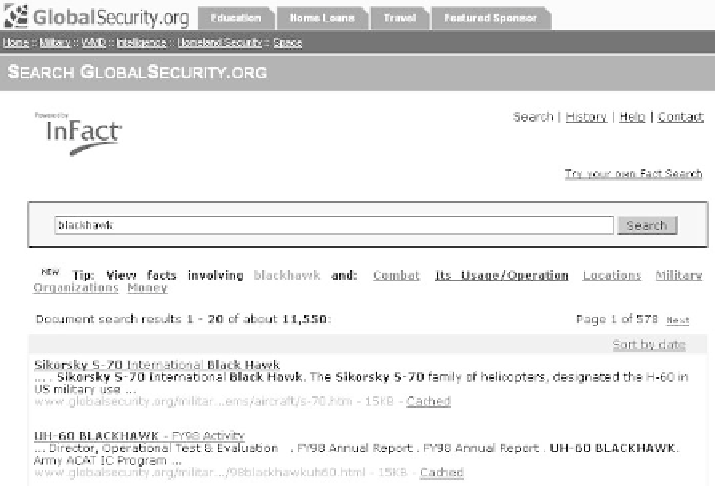
Fig. 5.5.
Keyword searchresult and automatic tip generationwithInFactinre-
sponse to the keyword query “blackhawk.”
5.4.3 UsabilityConsiderations
IndeployingInFact onthe GlobalSecurity.orgsite, our goal was toserve the infor-
mationneedsofawidecommunity ofusers, the majority ofwhichare accustomed
tostraightforward keyword search. Therefore, onthissite, by default,InFactacts
as akeyword search engine. However, we also started experimenting with ways to
progressivelymigrate users away fromkeyword search and towards naturallanguage
search or “fact search.” With reference toFigure 5.4, users approaching thesitecan
enter InFactqueries fromthesearchboxinthe upper left,or click onthe HotSearch
link. Thelatter executes apredefinedfact search, whichis particularlypopular over
an extendedtime period (daysor evenweeks). The HotSearchiscontrolledbyGlob-
alSecurity.orgstaff, and isoutside thecontrol ofthegeneral user. However,once in
theInFact searchpage (Figure 5.5), the user can execute fact searches explicitlyby
using theIQL syntax. TheIQL syntax is fullydocumentedintheInFactHelppage.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search