Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
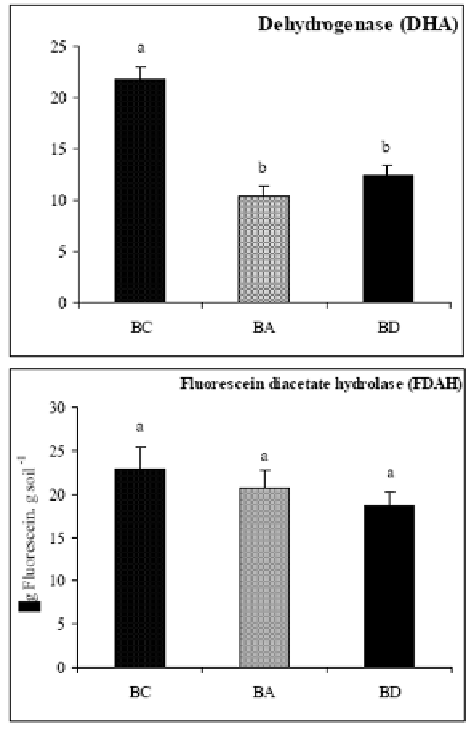
In our study FDA assay was performed according to Adam and Duncan (2001).
However, no relationship where detected between soil contamination and FDA assay, since
all soils presented similar activities of these enzymes (Figure 4).
Figure 4 .Dehydrogenase activity (μg TPF g soil
-1
) determined over a period of 24 hours; and FDA
activity (μg Fluorescein g soil
-1
) determined over a period of 20 minutes, in BC, BA and BD soils. Data
are mean ± SE of 30-40 replicate measurements. Different letters indicate means that are significantly
different (P< 0.05) from each other.
Catalase is an intracellular enzyme found in all aerobic bacteria and in most facultative
anaerobes. Catalase activity in soils is considered an indicator of aerobic microbial activity
and has been related to both the number of aerobic microorganisms and to soil fertility
(Garcia and Hernández, 1997).
In this work catalase activity varied significantly (P<0.05) between control soil (BC) and
BA and BD soils. The soil with higher organic matter content (BD) was the same where
catalase activity was lower (Figure 5). This is in disagreement with Kizilkaya et al. (2004)
who related increases of catalase activity to the higher soil organic matter content. Heavy
metal contamination negatively influences catalase activity, since catalase is a metaloenzyme,
and the presence of heavy metals such as Ni and Cu inhibits its activity (White and White,
1997). Kizilkaya et al. (2004) reported that catalase activity is reduced by heavy metal