Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
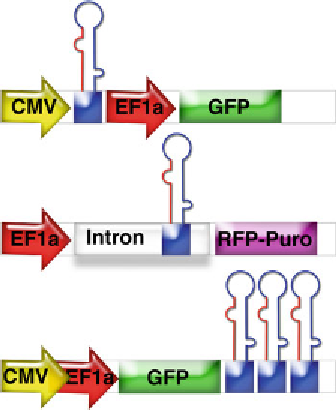
Fig. 3
The structure of the commercial lentiviral vectors for the miRNA expres-
sion. The two-promoter vector from System Biosciences (
upper panel
) utilized
the CMV promoter to express miRNA and the human EF1
promoter to express
the fl uorescent marker GFP. In this case, the pri-miRNA does not contain the
marker mRNA. The lentiviral vector from Biosettia (
middle panel
) uses only one
promoter, EF1
α
, to express both miRNA and RFP-Puro fusion marker. Interestingly,
the vector incorporates miRNA into an intron mimicking the preferred location of
endogenous miRNA. The pri-miRNA will include the miRNA as well as the marker.
In this case, the marker mature mRNA is released by splicing, and pre-miRNA is
excised by Drosha. The company claims that the intronic location of miRNA is
advantageous for the good expression of the marker. The lentivirus vector from
Invitrogen (
lower panel
) has a simple one-promoter arrangement with GFP posi-
tioned immediately after the promoter. The pri-miRNA includes the GFP sequence
followed by miRNA sequence. The pre-miRNA is excised by Drosha and follows
the miRNA-processing pathways, whereas GFP mRNA is translated until the stop
codon. Two promoters shown illustrate that the system offers a choice of the
CMV and EF1
α
promoters as well as the possibility to use any Pol II promoter of
choice. Multiple miRNAs shown indicate the possibility of miRNA “chaining”
offered by the vector
α
translation of the marker is initiated at IRES. Some lentiviral vec-
tors express GFP under a separate promoter (two promoter sys-
tem), for example, CMV for the miRNA transcription and EF1
for
GFP or other marker (Fig.
3
). The third critical element of the basic
lentiviral vector is a region containing multiple cloning sites allow-
ing for the subcloning of miRNA of interest. Alternatively, as in the
Invitrogen system, miRNA-containing cassette is assembled in an
entry vector (purely cloning nonmammalian expression vector) and
then transferred to the lentiviral vector via homologous recombina-
tion reaction (swapping of the DNA sequences located between
specifi c sequences, or recombination sites).
α
Search WWH ::

Custom Search