Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
HII
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
1200 1300 1400 1500 1600 1700 1800 1900 2000 (year)
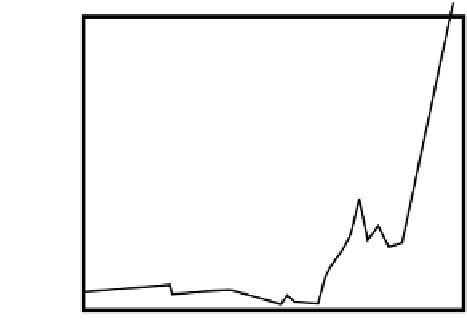
Figure 10.8
Historical change of Human Influence Index (HII). (From Gong et al., 1999. With permission.)
Diagnostic Horizons of Anthrosols
Under the condition of submerged cultivation, with the alternation of redox and fertilization,
anthraquic horizon sequence has been formed, which includes anthraquic epipedon and hydragric
horizon. Under the upland farming systems with irrigating siltigation or cumulating cultivation or
planting vegetable cultivation, irragric epipedon, cumulic epipedon, or Ýmic epipedon has been
formed (Gong, 1984; Gong and Zhang, 1998; Gong et al., 1999).
Anthraquic Epipedon
The anthraquic epipedon is an anthropic surface horizon that includes the cultivated horizon
and the plow-pan formed under the condition of submerging cultivation (Figure 10.9). An anthraquic
epipedon has all of the following characteristics:
¤a thickness of 18 cm or more
¤
in most years, when the soil temperature is more than 5 C, an anthrostagnic moisture regime for
at least 3 months per year
¤
in most years, when soil temperature is more than 5 C, in the upper part of the epipedon (the
cultivated horizon), puddling for at least half a month per year due to soil mixing by submerging
cultivation
¤
under a submerged condition, a color value (moist) of 4 or less and a chroma (moist) of 2 or less
and a hue of 7.5 YR or yellower showing GY, B, or BG
¤
more rusty spots and rusty streaks after drainage
¤
in a dry condition after drainage, a ratio of the soil bulk density in the lower subhorizon (plowpan)
to that in the upper subhorizon (cultivated horizon) being 1.10 or more
Hydragric Horizon
The hydragric horizon is a subsurface horizon formed by the reductive leaching of iron and
manganese from surface layer or reductive upward movement of iron and manganese from under-
lying gleyic layer, and the successive oxidation of reduced materials. It meets the following
requirements:
¤a thickness of 20 cm or more with the upper limit located in the bottom of the surface layer
¤having one or more of the following redox features: