Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 2.10 The injury degrees of shockwaves for staff
Super pressure of shockwaves (with-
out booster) (kg/cm
2
)
Injury degrees
0.02
-
0.03
Slight (slight contusion)
0.03
0.05
Medium (hearing injury, medium contusion, mild
bleeding of organs, fractures)
-
0.05
0.10
Severe (severe contusion of organs, may cause death)
-
>1.0
Extremely severe (may cause death in large extent)
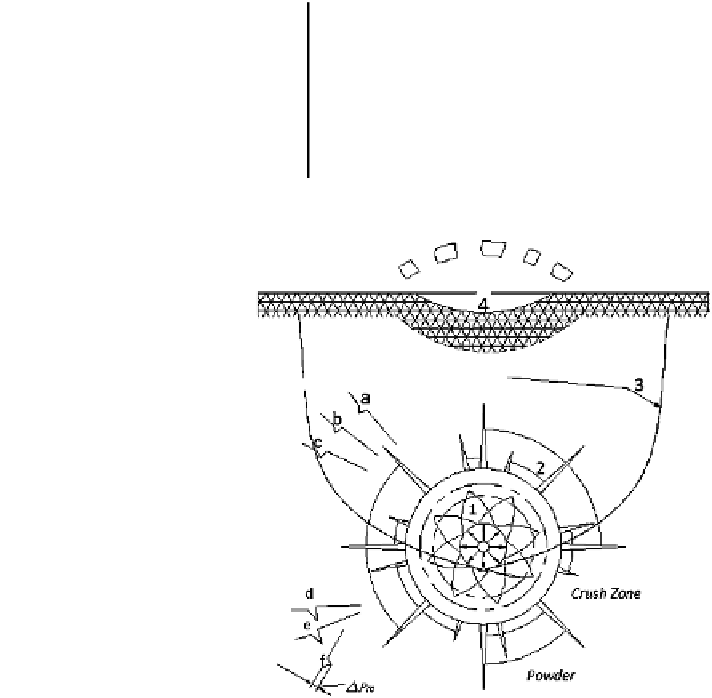
Fig. 2.34 Explosion of liquid
explosives inside the rocks
and soil. 1 Crush zone; 2
crack zone; 3 permanent and
elastic deformation zone; 4
top free soil subsidence
because of re
ective waves. a,
b, c the sequence change of
pressure waves in the dry soil;
d, e, f the sequence change of
pressure waves in the rocks
fl
of rocks result in
fine cracks with compression. In this zone, the shock waves
transport with super sonic velocity.
Following the shock wave fronts travel far away from explosion center, the
energy distributes the space, which is linearly proportional to the cubic of distances.
So the pressure of shock waves decreases rapidly. At certain distance, the super
pressure is lower than the limit strength of rocks, and the deformation changes with
crushing and slip surface disappearing, the structure of rocks and soil kept. Under
the compression of shock waves, the rocks and soil move out radially. Each cycle
unit is under drawing stress. When this drawing stress is larger than the limit tensile
strength of rocks and soil, the radial cracks from explosion center to out are pro-
duced. This zone is destruction zone, which is much larger than above two zones.
Because of inertia, after the explosion shock waves leave the explosion zone, the
earth continues to leave from the explosive places and lasts some time. It induces
the negative pressure of explosion zone, and the transportation of sparse waves.