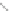Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
azido compounds react with alkene to produce
five-membered triazole cycles.
Under the catalysis of Lewis acids, organic azido compounds have cycloaddition
with ketone, and react with X
Y triple bond compounds (nitriles) to form tetra-
zoles. Organic azido compounds react with X=Y double bond cumulenes with
hetero atoms (e.g., isocyanate, isothiocyanate, or carbodiimide) to produce oxazoles
with nitrogen heteroatoms.
Huisgen cycloaddition of organic azido compounds and alkyne is 1,3-dipolar
cycloaddition of azido compounds and terminal or central alkyne to produce 1,4- or
1,5-substitution triazoles. Their reaction process is below.
≡
N
+
R
R
N
N
N
-
N
N
N
N
N
+
H
R'
R'
R'
1,5-substitution triazole
1,4-substitution triazole
s study in 1960s makes Huisgen cycloaddition completely understood
and a kind of important novel reactions [
9
]. In early twenty-
Huisgen
'
rst century, Sharpless
and Meldal improved Huigen
s reaction independently through using Cu(I) catalyst
to stereoselect 1,4-substitution triazoles. (1) This reaction is
'
finished quantitatively,
and the yield is close to 100 %. (2) This reaction is highly tolerated for function
groups, and not sensitive for chemical structures of molecular ligans. Other function
groups do not need be protected. (3) The reaction can be conducted in all solvents.
(4) The reaction can be operated at room temperature, which helps keep the activity
of biomolecules. (5) This reaction occurs not only in homogeneous phases, but also
on the intersurfaces, for example, the intersurfaces of liquid
solid, liquid
liquid, or
-
-
solid
solid. These features make the reaction play an important role in connection
of ligands and synthesis blocks, surface modi
-
cation of macromolecules and
nanomaterials, coupling of biomolecules, new drug development, etc.
6.1.2.2 Application of Azido Compounds in Synthesis of Triazoles
and Amine-Group Compounds
Triazoles are a kind of nitrogen containing heterocyclic compounds with stable
chemical properties. Compared to amides, triazoles do not hydrolyze. Unlike
benzene or heteroaromatic compounds, triazoles are seldom oxidized or reduced.
The application of triazoles varies from antiseptics, herbicides, and microbial
inhibitors of agriculture to light stabilizers,
fl
fluorescent brighteners, preservatives,
and
fire retardants of industry. Triazoles are used in drug delivery and nano devices
of functional macromolecules area, and applied in oligonucleotide preparation, cell
culture, anti-in
ammatory and antiretroviral therapy, HIV protease inhibitors, and
messenger ribonucleic acid (m RNA) hairpin loop speci
fl
c ligands of medical and
biology technology. Triazoles with metabolic inertia and donor
acceptor of mul-
tiple hydrogen bonds are mock objects of peptide bonds. The molecules synthesized
-