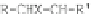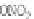Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 5.3
Constants for
five nitrate esters
Esters
Viscosity (
g
)
Density
d
16
16
Refractive index
n
21
:
2
D
Temperature (
°
C)
Poise
Nitroglycerine
5.1
1.033
1.5985
1.472
20.0
0.352
55.0
0.0875
Ethanediol dinitrate
7.1
0.0633
1.4918
1.446
20.0
0.0423
54.4
0.0198
1,3-propylene glycol
dinitrate
6.3
0.0940
1.4053
1.448
20.4
0.0550
54.4
0.0275
Diethylene glycol
dinitrate
6.0
0.133
1.3890
1.4505
20.4
0.0727
54.4
0.0337
Triethylene glycol
dinitrate
6.0
0.257
1.3291
1.4542
20.3
0.119
54.2
0.015
5.1.2.1 Dipole Moment
Dipole moment (
) is one of the main parameters to judge the stability of constants.
In general, the dipole moment of alkyl nitrates is relatively easy to be measured.
The
μ
of methyl nitrate is 2.73 Debye. It seems no distinct connection between the
chain lengths of alkyl nitrates with their
μ
μ
values. The dipole moment of some
20
1
nitrate esters can be calculated through their
ʵ
and
g
. The calculation results are
shown in Table
5.4
.
Based on the point of view, the discrimination of the dipole moments between
pure materials and benzene solution is due to the formation of trans optical isomers
in benzene solution.
Through the study of dipole moments [
19
], pentaerythritol tetranitrate might
have optical anomers. The general formula of nitrate esters can be given by Infrared
adsorption spectroscopy as:
If X = ONO
2
,NO
2
, CN, I, Br, or Cl, the nitrate esters have optical anomers.
5.1.2.2 Spectroscopic Features of Nitrate Esters
A band at 270 nm in UV spectra can be observed for O-nitro groups, similar with
the band of C-nitro groups. Though there are few studies on UV spectroscopy of