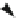Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Based on the sodium nitrite and dimethyl sulfate replacement reaction to produce
nitromethane, Some [
31
] used tetrabutylammonium bromide as a catalyst to achieve
nucleophilic substitution to improve the conversion. And the obtained purity of
nitromethane can be up to 99.9 % with methyl nitrite as the byproduct. The main
raw materials are dimethyl sulfate and sodium nitrite with a feeding molar ratio of
1:2, and its synthesis mechanism is:
ð
Þ
2
SO
4
þ
2NaNO
2
!
CH
3
NO
2
þ
"þ
CH
3
CH
3
ONO
Na
2
SO
4
This overall chemical reaction can be explained step by step as the following:
The
first methylation step:
ð
CH
3
Þ
2
SO
4
þ
NaNO
2
!
CH
3
NO
2
much
ð
Þþ
CH
3
ONO little
ð
Þ"þ
CH
3
NaSO
4
The second methylation step:
CH
3
NaSO
4
þ
NaNO
2
!
CH
3
NO
2
much
ð
Þþ
CH
3
ONO little
ð
Þ"þ
Na
2
SO
4
The hydrolysis of dimethyl sulfate under basic or acidic conditions:
2CH
3
OH+SO
4
2-
OH
(CH
3
)
2
SO
4
H
2CH
3
OH+H
2
SO
4
CH
3
OH+Na
2
SO
4
OH
CH
3
NaSO
4
H
CH
3
OH+NaHSO
4
Reactions of nitromethane with acid and base:
CH
3
NO
2
þ
HCl
!
NH
2
OH
HCl + CO
"
CH
3
NO
2
þ
NaOH
!
CH
3
OH
þ
NaNO
2
Reactions of nitrous acid:
H
N
2
O+H
2
O
ONO+
H
CH
3
ONO
ONO+(CH
3
)
2
SO
4
CH
3
NO
2