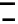Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
c
2a
þ
A
¼
100
%
ð
3
:
2
Þ
2
or
2c
4a
þ
A
¼
Þ
100
%
ð
b
cient is the percentage of oxygen contained in the explosive
over the required oxygen to completely oxidize carbon and hydrogen in the
explosive. Same as the oxygen balance, it is also used to measure the relative
relationship between oxygen content of the explosive and its
Thus, oxygen coef
flammable element
content. Similarly, it is related to detonation products of the explosive.
The following two examples are going to show the calculation of oxygen
coef
fl
cient.
(1) The oxygen coef
cient of nitroglycerine (C
3
H
5
O
9
N
3
) is:
9
A
¼
100
¼
105
:
9
%
5
2
2
3
þ
(2) The oxygen coef
cient of mixed explosive with nitric acid and toluene (nitric
acid of 86, 14 % of toluene) is:
3
1
A
1
HNO
3
ð
Þ¼
2
100
%
1
A
2
toluene
ð
Þ¼
100
%
þ
7
2
2
7
!
3
1
2
35
A
¼
A
1
þ
A
2
¼
2
þ
100
% ¼
605
:
7
%
3.1.2 Influence of Oxygen Balance on Explosive Properties
The liquid explosive, with zero or near zero oxygen balance, has relatively large
detonation strength and detonation intensity [
3
5
]. In Table
3.2
, a set of oxygen
balance, detonation strength, and detonation intensity test data of nitric acid
-
toluene
liquid explosive mixture was listed. The experiment results showed that nitric acid
-
-
toluene liquid explosive mixture, when the composition was close to zero oxygen
balance, had relatively high explosive property; while, had relatively low explosive