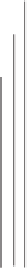Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
R
f
is applied to thin-layer chromatography, while
R
t
is applied to GC and
HPLC. For identification purposes the
R
f
values of pure samples of all the com-
pounds to be found in the unknown are determined and are used to “iden-
tify” these same compounds in an unknown mixture. The
R
f
of a compound is
determined by placing a spot of sample on a thin layer sheet slightly above
the bottom, placing the TLC sheet in the developing chamber with the appro-
priate elutant and allowing the elutant to raise the thin layer until it is close
to the top (but never at or over the top). The distance from the site where the
spots were placed on the plate to top of the plate where the elutant stopped
is recorded. This number is then divided into the distance the spot moved from
the beginning as shown in Figure 9.8.
The distances should always be measured from the starting point, which is
where the original mixtures were spotted both from and to the midpoint of the
spots. The determination of the
R
f
values of five spots on a thin-layer chro-
matogram is given in Figure 9.6. The
R
f
values of the spots are listed in Table
9.4. The material in spots
A
2
and
B
2
are expected to be the same since they have
the same
R
f
and the chromatogram was run under exactly the same conditions.
R
t
is used in the same manner as is
R
f
except that it is the retention time of
components in the GC or HPLC column (see Figure 9.6). The time can be
measured from the time of injection to the time when the top of the peak
elutes from the column. Another approach is to include a compound that is
not retained by the solid or liquid phase in the injection and its peak used are
the starting time for measuring the time for each peak to exit the column. Two
compounds exiting the column at the same
R
t
will be assumed to be the same
compound. Often
R
t
values are used for identification, although only a spec-
troscopic method can truly be an identification method.
Another method is to chromatograph the unknown and determine the
R
f
values of the components present. When a compound is “identified” by its
R
f
,
Solvent (elutant) front
B3
12 cm
A2
B
2
9cm
15 cm
A1
3cm
B1
2cm
Start
AB
Start
Figure 9.8.
Thin layer at start (left) and after development (right). Right chromatogram shows
the distance that the elutant and spots moved during the development of the chromatogram.