Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
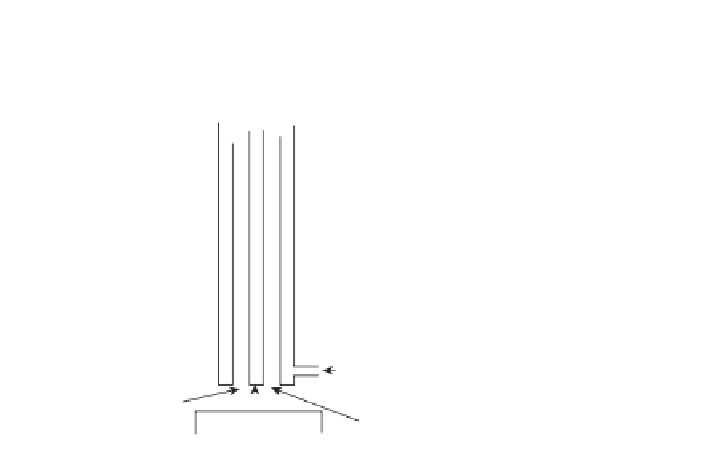
Induction coil
Quartz
tubes
Argon coolant
flow
Argon
support
gas
Argon
support
gas
Argon - sample
aerosol
Figure 8.5.
Left is a diagram and on the rights is a photograph of an ICP torch.
being analyzed. ICP is carried out using a separate instrument and generally
has a significantly higher sensitivity than do flame instruments. There are
a number of hyphenated variations on the basic EM and ICP instrumentation
such as ICP-OES [(ICP optical emission spectroscopy); also some-
times referred to as ICP-AES (atomic absorption spectroscopy)] and ICP-MS
(ICP-mass spectroscopy).
AA and ICP instruments can be equipped with multiple detectors so that
analyses for more than one element at a time can be accomplished [3,9-13].
8.5.2.
Atomic Absorption
In atomic absorption light emitted by the element of interest, from a hollow
cathode lamp (HCL), is passed through the flame of an atomic absorption
spectrometer (the same instrument is used for EM except now configured for
the AA mode). In this case the same burner and flame as described above and
shown in Figure 8.4 is used. The source of the light is a hollow cathode lamp,
also shown in Figure 8.4, where the cathode is made of the element of inter-
est and thus, when excited, emits the analytical wavelengths of light needed
for the analysis of that element. In a majority of cases a different lamp will be
needed for each element for which an analysis is required. The amount of light
absorbed by the element in the flame is directly proportional to the amount
of that element present. Atomic absorption is significantly more sensitive than
flame emission for most metals [14,15].