Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
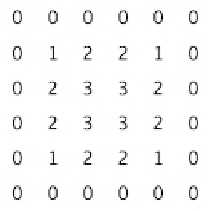
FIGURE 5.3
Resulting 6
×
6 reduced grid.
contract accordingly). Of course, such methods may not be possible depending on
the aim of the model, and certain agents may not be amenable to aggregation. In
particular, this strategy tends to be more difficult to implement in models with a high
level of spatial heterogeneity or a high level of specification at the agent level.
Whereas scaling requires the dimensions of the model to be reduced (and other
model parameters accordingly scaled), aggregation generally requires reconstruction
of the model, since the scope of the model is altered as the agent structure is reformu-
lated. In that sense, aggregation can be more involved than scaling. On the other hand,
the long-term goal of both techniques is to improve run time and reduce computation,
so the extra steps may be well worth the effort. A combination of both techniques can
provide substantial decreases in run time and simplification without loss of pertinent
model dynamics or detail.
The following exercises refer to the modified Rabbits and Grass model,
Rabbits
Grass.nlogo
, available at
http://admg.vbi.vt.edu/software/rabbitsgrass-netlogo
-files/
. Please read the
Info
tab to familiarize yourself with the details of this model.
Exercise 5.13.
Run the model with the default values for
world-size
44,11, 5.
In each case, after the simulation ceases, take a snapshot and examine the population
plots. What differences do you notice? What is the benefit of decreasing the world
size? How would you determine the smallest world size that you could use to obtain
reliable results?
Exercise 5.14.
Note in the cost function that we multiply the rabbit cost by
150
initial
−
rabbits
. Why is this? Why do we not multiply the poison cost by the
same factor?
Exercise 5.15.
Turn
scale-rabbits?
off and run the model several times at
various sizes. What differences do you notice in the population graphs? What is
the effect of this option? Are results at smaller sizes more or less reliable when
scale-rabbits?
is off?
Exercise 5.16.
When
scaling-rabbits
is on and the world size is reduced,
the rabbits become larger (graphically). Is reducing the number of rabbits an example
of scaling or of aggregation? Justify your answer.




Search WWH ::

Custom Search