Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Goal
Delegated
Adopted
'
PLAN
1
action
action
action
Y
X
Figure 7.13
Sub-help
attitudes in that specific task (a sort of selftrust). Suppose that
Delegates(Ag
1
Ag
2
τ
)
and
τ
is
included in a more general
Ag
1
's plan aimed at achieving goal
g
through a complex action
α
.
α
α
τ
=
α
,g
). We have three main delegee's adjustments:
Moreover,
Dom-c(
)
,
τ
=
(
α
,g),
and
(
Reduction of help
Here the
delegee provides less help on
τ
than delegated
.If
Adopts
(
Ag
2
Ag
1
τ
1
)
∧
Dom
-
c
(
αα
1
)
(7.9)
with
α
1
,g
1
)
, the delegee reduces the task to a subpart of the requested one (see Fi-
gure 7.13). For example
Ag
1
delegates
Ag
2
to prepare a main course for a dinner and bring it
to her house.
Ag
2
only buys the ingredients but does not cook them.
A sub-help is not necessary a help (although lower than expected). Maybe the realized
action and the achieved subgoal are completely useless (in a plan the coordination among the
actions and their results are also very important).
For example, in the case of the previous example, maybe the ingredients cannot be cooked
at
Ag
1
's house because of a problem with the kitchen.
Extension of help
τ
1
=
(
Here the delegee provides more help on
τ
than delegated. If
α
α
1
)
OR
(
α
≡
α
1
))
Adopts
(
Ag
2
Ag
1
τ
1
)
∧
Dom
-
c
(
α
1
α
)
∧
(
Dom
-
c
(
(7.10)
with
α
1
,g
1
)
; the delegee goes beyond what has been delegated by the client without
changing the delegator's plan (Figure 7.14). In fact, the delegee chooses a task that satisfies a
τ
1
=
(













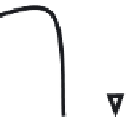





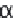


Search WWH ::

Custom Search