Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
τ
,
similarity given his knowledge of their features) on a set of tasks
T1
≡
{
τ
,
...
,
τ
n
he can
}
trust each of the agents included in
AG1
on each of the tasks included in
T1
.
The fourth case (
caseD
) we consider is when
Ag
X
knows both
τ
's properties and
Ag
Y
's
features, and they trust
Ag
Y
on
(in this case for inferential reasoning on the match between
properties and the features). In more formal terms:
τ
d1)
Trust
Ag X
(
Ag
Y
,τ
)
d2)
Bel
Ag X
(
f
AgY
≡{
f
1
,...,
f
n
}
)
p
1
,...,
p
k
}∪{
d3)
Bel
Ag X
(
τ
≡{
p
1
,...,
p
m
}
)
Ag
X
can both believe:
that a different (but in some way analogous) agent
Ag
Z
is trustworthy on the task
τ
(gen-
eralization of the agent) starting from the cognitive elements (d1 and d2) and from the
knowledge of
Ag
Z
's features; or
that
Ag
Y
is trustworthy on a different (but in some way analogous) task
τ
(generalization
of the task) starting from the cognitive elements (d1 and d3) and from the knowledge of
τ
properties; or again
that a different (but in some way analogous) agent
Ag
Z
is trustworthy on a different (but in
some way analogous) task
τ
(generalization of both the agent and the task).
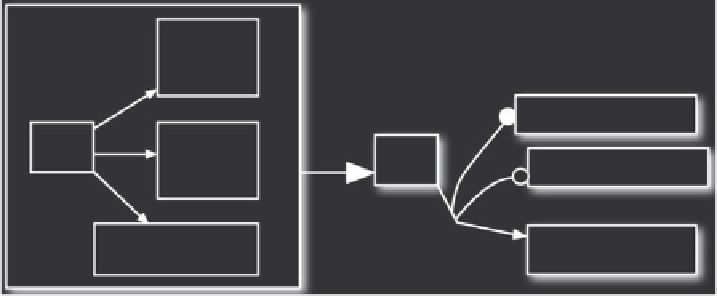
So we can conclude (see Figure 6.16) that in the case (
D
) both task and agent generalization
is possible: in fact the set
(d1, d2, d3) permits both agent and task generalizations.
Note that we have considered in all the studied cases (
a1, b1, c1
, and
d1
) the fact that
Ag
X
trusts Ag
Y
on the initial task
. In fact, in case of
distrust
(or mistrust) we could receive
analogous utility (in cases
B
,
C
and
D
) for the distrust (or mistrust) generalization to the other
agents or tasks. In other words,
Ag
X
on the basis of his experience with
Ag
Y
on task
τ
τ
could
distrust agents similar to
Ag
Y
or/and tasks similar to
.
The case in which, from a specific knowledge about agents, tasks and their matches, a
trustor can infer complementary features or properties
contradicting
their previous positive or
τ
τ
Ξ
Generalization
on tasks
Ag
Y
Ξ
AG
X
AG
X
Generalization
on agents
Trust
(Ag
Z
,
τ
')
Trust
(AgY,
τ
)
AgX
AgX
Figure 6.16
Generalization in case
Ag
X
knows both task's properties and trustee's features. (Repro-
duced with kind permission of Springer Science+Business Media
C
2008)


Search WWH ::

Custom Search