Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
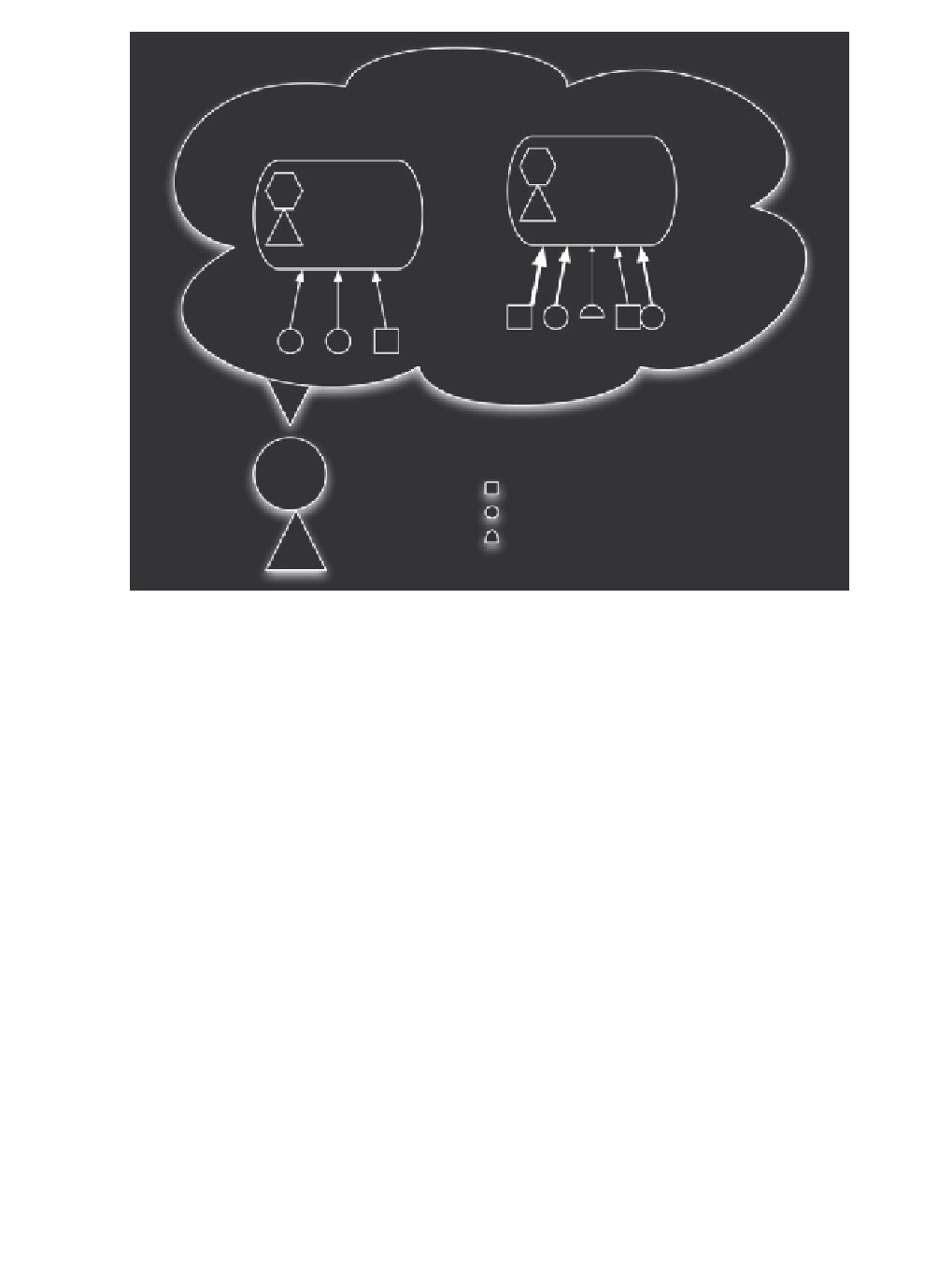
BEL = 0.8
BEL = 0.2
= 0.2 - 0.3
= 0.7 - 0.8
Y
Y
Ability
Ability
= reasoning
= experiences
= a priori judgements
X
Figure 3.1
Quantifying
X
's Beliefs about
Y
's ability
failures of the various components of trust). Finally, we will introduce different quantitative
thresholds linked with the different quantitative dimensions included in our cognitive model.
In sum,
the quantitative dimensions of trust are based on the quantitative dimensions of
its cognitive constituents
. For us, trust is not an arbitrary index just with an operational
importance, without a real content, or a mere statistical result; but it is derived from the
quantitative dimensions of the pertinent beliefs.
3.2 Relationships between Trust in Beliefs
and Trust in Action and Delegation
The solution we propose is not an
ad hoc
solution, just to ground some degree of trust. It
instanciates a general claim. Pears (Pears, 1971) points out the relation between the
level of
confidence
in a belief and the likelihood of a person
taking action based on the belief
:'Thinkof
the person who makes a true statement based on adequate reasons, but does not feel confident
that it is true. Obviously,
he is much less likely to
act on
it, and, in the extreme case of lack
of confidence, would not act on it
' (p. 15) (We stressed the terms clearly related to theory
of trust).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search