Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
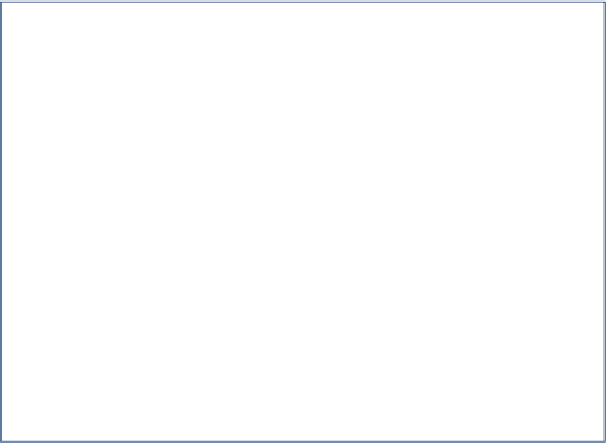
Network boundary
255
2. Bacteria
116.6
75
11,184
5,205
1,600
3,275
3. Detritivores
60.0
2,309
8,881
1. Plants
285.0
5. Detritus
3579.4
200
300
1,814
370
2,003
3,109
4. Carnivores
17.0
635
860
203
Fig. 5.3 Network diagram of Cone Spring ecosystem energy flows [
10
]. All flows are in kcal/m
2
/
year. Biomasses are in kcal/m
2
.
Green arrows
are exogenous boundary inflows.
Black arrows
are
exports of useable energy.
Red ground
symbols represent metabolic energy loss
Table 5.2 Results of the flow analysis partitioning for
Cone Spring ecosystem. Values represent the fraction
of total system throughflow for each mode
Mode 0
0.386
Mode 1
0.522
Mode 2
0.092
Mode 3
0.522
Mode 4
0.386
And the integral flow matrix is:
2
3
1
0
0
0
0
4
5
0
:
958
1
:
207
0
:
374
0
:
186
0
:
545
N
¼
0
:
434
0
:
547
1
:
169
0
:
084
0
:
247
0
:
199
0
:
251
0
:
092
1
:
039
0
:
113
0
:
031
0
:
039
0
:
014
0
:
161
1
:
018
Looking at
Table 5.2
,itisseenthatover38%oftheflowcomesdirectlyto
a node from the first instant across a system boundary and 52% of the flow
originates from one compartment and enters another compartment for the first
time without cycling. Slightly over 9% of the total energy flow is material that has