Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
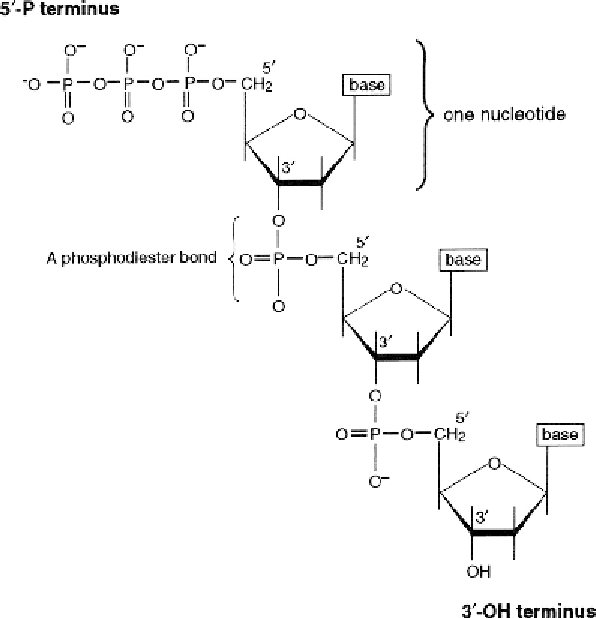
Figure 1.4
A nucleoside consists of a sugar joined to a base. It becomes a nucleotide (nt) when a
phosphoric acid group is attached to the 5
′
-carbon of the sugar. Nucleotides link together by phos-
phodiester bonds to form polynucleotides.
Because there are no restrictions on the nucleotide sequence, a polynucleotide
of just 10 nt long could have any one of 4
10
(or 1,048,576) different sequences.
This ability to vary the sequence is what allows DNA to contain complex genetic
information.
1.6 The Molecular Structure of RNA
RNA also is a polynucleotide and has multiple functions in the cell (
Richter and
Treisman 2011, Tuck and Tollervey 2011
), including the role as mRNA. RNAs dif-
fer from DNA in two important ways. First, the sugar in RNA is
ribose
(
Figure
1.2
). Second, RNA contains the nitrogenous base
uracil
(U) instead of thymine
(
Figure 1.3
). The four nucleotides that polymerize to form RNA are adenosine
5
′
-triphosphate, guanosine 5
′
-triphosphate, cytidine 5
′
-triphosphate, and uri-
dine 5
′
-triphosphate, abbreviated as ATP, GTP, CTP, and UTP or A, G, C, and U,