Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
and Smagghe 2010, Perrimon et al. 2010, Yang et al. 2011, Yu et al. 2012
).
RNAi methods for pest control could involve developing transgenic insects
that carry small hairpin RNAs (shRNAs), small hairpin microRNAs (shmiRNAs),
or long ds RNAs because they allow for controlled or continuous expression of
small transcripts in the cell that contain both the sense and antisense strand
complementary to the targeted mRNA (
Perrimon et al. 2010
). These will need
to be maintained as stable extrachromosomal copies or stably integrated in the
genome as transgenes. shmiRNAs are considered more effective in knocking
down target mRNAs than shRNAs.
Systemic RNAi occurs in some insects, but not others (
Price and Gatehouse
2008, Tomoyasu et al. 2008
).
Whyard et al. (2009)
showed that ingested ds RNAs
can act as species-specific insecticides when fed to
D. melanogaster
,
Tribolium
castaneum
,
Acyrthosiphon pisum
, and
Manduca sexta
when each insect was fed
species-specific ds RNAs targeting vATPase genes. The ds RNAs had to be encap-
sulated into liposomes to ensure uptake in the
D. melanogaster
diet, but the
other species tested did not need this treatment.
A
B
C
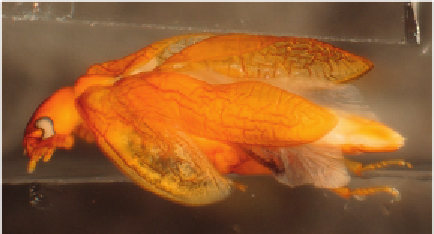
Figure 14.1
A) Normal
Tribolium castaneum
adult. B) RNAi of the Hox gene
ultrabithorax
in larvae
leads to adults with two pairs of elytra. C.) RNAi of
Scr
(
Sex combs reduced
) results in beetles with two
pairs of elytra and membranous hind wings. (Photos courtesy of Y. Tomoyasu.)