Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
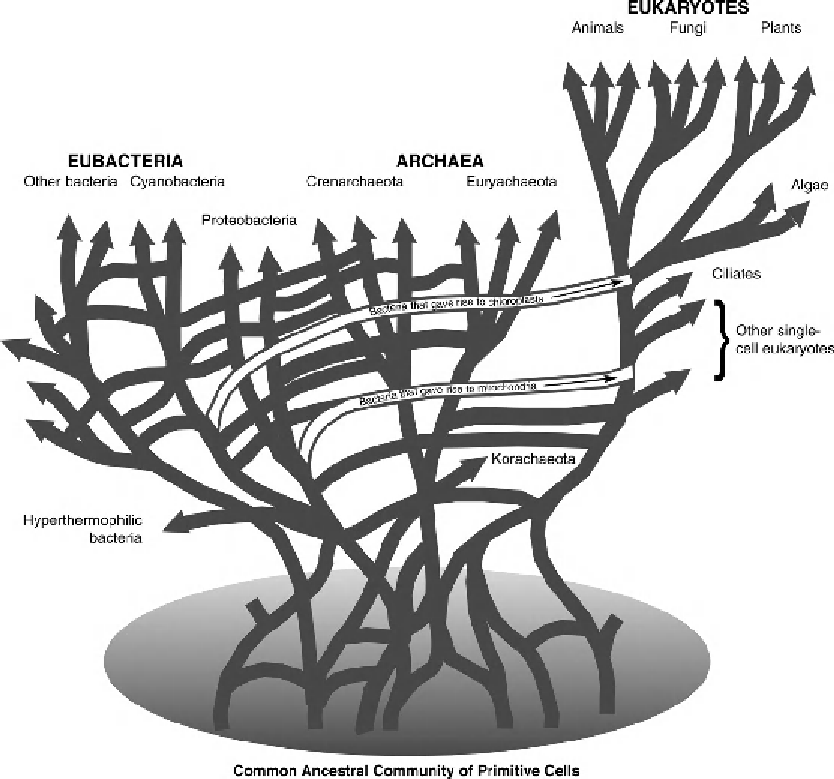
Figure 12.6
Molecular phylogenies support the concept of a “web of life” in which gene exchange
and horizontal gene transfer have had significant effects on the evolution of the Archaebacteria,
Eubacteria and Eukaryota. The evolution of life has involved multiple events of horizontal gene
transfer between the domains, including incorporation of Eubacteria that gave rise to chloroplasts
and mitochondrial, as well as transmittal of vertically transmitted archaeal genes. A “linear” view of
the evolution of life had to be modified once genome analyses indicated the relationships between
the domains were more complex. (Modified from Doolittle 2000.)
with genes arranged in operons. Archaebacteria and the Eukaryota have gene-
expression machinery with shared traits. Chimeric genomes could have devel-
oped only if lateral transmission of genes (or genomes) took place across species
boundaries (
Katz 1999
).
Doolittle (1998)
proposes that gene swapping (leading