Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
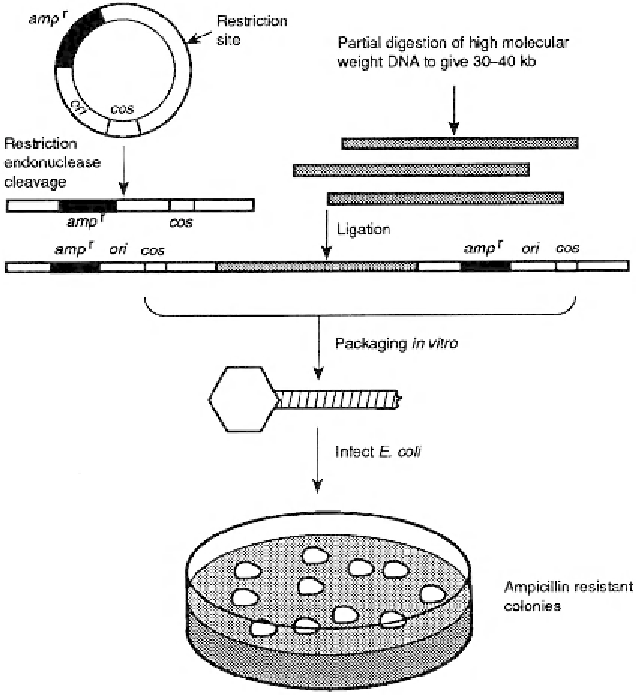
Figure 6.7
Outline of procedures used in cloning with a cosmid vector. This vector contains a
cos
site, a restriction site for inserting exogenous DNA, and a gene for ampicillin resistance. Exogenous
DNA is cut with an appropriate restriction enzyme, as is the vector. The vector and exogenous DNA
are ligated together, producing a recombinant molecule of 37-52 kb that can be packaged in
λ
by
in
vitro
packaging. The packaged vector infects
E. coli
, injecting its DNA into the host, where it circular-
izes and multiplies.
Escherichia coli
cells that receive the cosmid are distinguished from cells that are
not infected by their ability to survive on media containing ampicillin.
the
cos
site (
Figure 6.7
). Cloning into cosmids is similar to cloning in
λ
. It involves
digesting exogenous DNA with a restriction enzyme, cutting the cosmid vector
with a compatible restriction enzyme, combining the two, and ligating them.
Once the exogenous DNA is inserted into the cosmids, cosmids are packaged
in a manner similar to that used with
λ
. Packaging the cosmid recombinants into
phage coats provides a useful method for selecting the size of the inserted DNA.