Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
This paper is divided into five sections. The second section provides a brief over
view on data collection methodology. In third section, the structure of the proposed
FLM is discussed in brief. The inference engine and fuzzy operators, and neuro-fuzzy
training procedure are also discussed. The fourth section discusses the FLM valida-
tion and analysis of results. Concluding remarks on the use of the FLM for estimating
the 85th percentile speed to set the speed limit are provided in the last section.
2
Data Collection
Spot speed survey were conducted on selected four sites for five different time periods of
the day, for a typical weekday and weekend and for both directions. The five time pe-
riods include both peak (AM, MD, PM) and off-peak periods (15 minutes within each
time period). Only passenger vehicles (excluding trucks and busses) were selected ran-
domly for the survey, keeping in mind that a minimum of 50 vehicles should be observed
for spot speed study on each selected road segments [20]. The 85
th
percentile speed of the
spot speed data was calculated for 40 different cases (4 sites*2directions*5 time periods)
for two days (one typical weekday and one weekend).
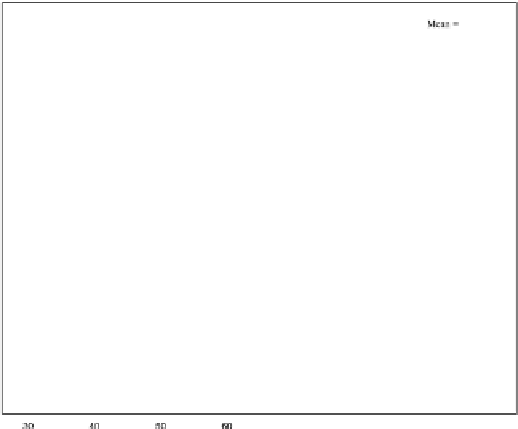
Fig. 1.
Observed spot speed distribution at Site 1 direction 1 for weekday (6:30 -7:30 AM)
The detailed road attribute data including the length of the road segment, number
of access points/intersecting links, number of pedestrian crossings, number of lanes,
traffic count and pedestrian count data (15 minutes count), and the current posted
speed limit for each road were collected. The length of Site 1 is 2.78 km, has 8 access
points and 3 pedestrian crossings on each direction. The traffic volume is relatively
high, but number of pedestrian is low on both weekday and weekend. Site 2 is 0.46
km long with 4 access points and 3 pedestrian crossings on each direction. This site