Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
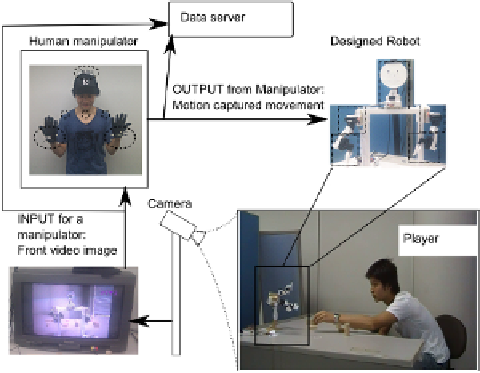
Fig. 5.
System implementation
5
Experiment
To research how our metho
robot, we compared human
tion using the PoRoS robot
the robot to decrease the
communication during inter
As a demonstrative task,
our method.
od evaluates the design and modalities of a nonhumanl
n-humanlike robot and human-nonhumanlike robot inter
t. In nonhumanlike robot interaction, we fixed the head
modalities for confirmation. We also prohibited ver
raction to emphasize the role of the head.
, we also setup the assembly of wooden blocks to evalu
like
rac-
d of
rbal
uate
5.1
Pre-evaluation for
Creating Evaluation Method
Humans nod for confirmati
ding has a regulatory role in
computer interaction [23]; [
At first, we examined wh
observing human-human in
and assembled three sets o
role of the manipulator. An
instructed the player to buil
in Fig. 6 consisted of five
ings in Fig. 6. Second, she/
the player how to construct
touch the blocks. The num
and eight and the construct
that human-human interact
taking happened according
ion. Nodding is conducted by the human head. Head n
n turn-taking in human-human communication and hum
[24].
hat kind of procedures humans apply to make buildings
nteraction. We gathered six participants for this evaluat
f pairs from them. One of the members of a pair took
nother member took the role of a player. The manipula
ld three kinds of buildings as shown in Fig. 6. All examp
kinds of blocks. First, the manipulator watches the bu
/he sat down in front of the player. Last, she/he instruc
the buildings. All manipulators were prohibited to dire
mber of instructions during the evaluation is between f
tion time is between 30 s and 60 s. The result confirm
tion is based on turn-taking strategies. Each pair's tu
to each user's nodding and shaking motion.
nod-
man-
s by
tion
the
ator
ples
uild-
cted
ctly
five
med
urn-