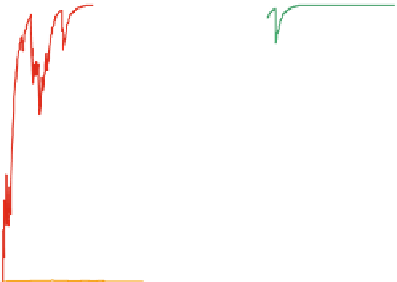Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
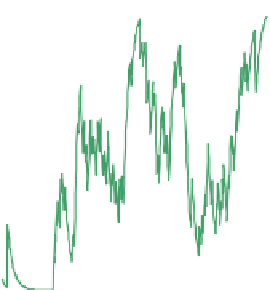
(i.e., the price maker agents) were characterized by a bidding price lower enough to
keep them out of the market. In this exploration process, they are characterized by the
slower convergence time, thus corroborating such conclusion.
1
Price Taker Agent
Price Maker Agent
Non Convergent Agent
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
Iterations
Fig. 7.
Convergence time-path for the different groups of interacting agents in ABM IPEX
5
Computational Experiments
Learning algorithms and agent-based models should stick to empirical criteria in order
to demonstrate that they are able to reproduce reality. In particular, at the micro-level,
learning algorithms should converge toward a price during the experiments, whereas,
at the macro-level, practitioners should be able to observe stylized facts and economic
emergent behaviors. Completed the learning convergence (see Section 4), we focussed
our attention to a set of computational experiments in order to understand the ability
of the framework to reproduce the emergent properties shown by the IPEX DAM at
macro-level. Firstly, we have chosen a reference power exchange setting (i.e., Gencos
and loads). In this respect, the scenario has been based on a real off-peak hour (i.e.,
hour 5 AM of Wednesday 16th December 2009) as during off-peak hour competition
among producers is generally limited and thus limiting the impact on the level of prices.
For the reference power exchange setting, we have performed 100 computational ex-
periments with different random seeds in order to analyze the ensemble results of the
same repeated game. Both agent convergence and system convergence have been ob-
served. While the former has been discussed in Section 4 and used as a validation proof
of the enhanced Roth-Erev learning algorithm, we now concentrate on the system con-
vergence. This type of convergence (or its lack) can be defined with respect to the
convergence of the PUN time path (i.e. the clearing price converge to a value after a
specific time which depends only from the participating agents). Indeed, the PUN is a
weighted-average of the Locational Marginal Prices by means of the inelastic loads and
an adequate representative of the market clearing and its convergence a good proxy that
the system has reached an equilibrium. In this context, we searched for the ”best per-
forming” economic-learning algorithm, i.e. the selection of the algorithm should have