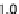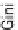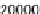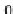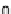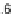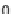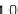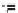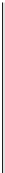Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
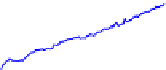
Fig. 6.
Influence on Gini coefficient in AG
For the second issue, we present our results in Figure 6. The Gini coefficient is
used as a measure of inequality of wealth distribution. Given a set of
N
agents' wealth
(
X
1
,X
2
,...,X
N
)
, the Gini coefficient
G
is defined as
N
j
=1
|
N
1
2
N
2
X
G
=
X
i
−
X
j
|
,
i
=1
where
X
=
i
=1
X
i
/N
.If
G
=0
, the wealth is completely even. If
G
is close to 1,
an agent has a monopoly on the wealth.
Figure 6(a) shows that the influence of memory size on the Gini coefficient. It means
that the smaller the memory size is, the wider the inequality of wealth becomes. If the
memory size is small, some successful agents earn much money and the others not. So
their mean asset values are widely distributed in the long run. Thus, the Gini coefficient
tends to be large.
Figure 6(b) shows that the influence of investment rate on the Gini coefficient. It
means that the larger the investment rate is, the wider the inequality of wealth becomes.
If the investment rate is large, the successful agents earn much money and the others
not. So their mean asset values are widely distributed in the long run. Thus, the Gini
coefficient tends to be large.
For the third issue, Figure 7 shows the price decreasing change distribution for sev-
eral games and NYSE, where NYSE is the Dow-Jones industrial average 20,545 data
(1928 /10/1 — 2010/7/26) in New York Stock Exchange. That is, the normalized de-
creasing change of price
and its distribution is compared. The straight
lines represent the Pareto indices. At a glance, the curves of ExAG and AG resemble
that of NYSE, which means their distributions are likewise. The Pareto index of ExAG
is also not far from that of NYSE.
For the fourth issue, we obtained the following results. Both ExAG and AG have
better values of skewness and kurtosis than MG does as shown in Tables 2 and 3,
where “stdev.” and “95% int.” mean standard deviation and 95% confidence interval,
respectively.
|
R
|
=
|
Δ
Price
/σ
|