Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Let the mounting medium set overnight at 4 °C. Leftover mounting medium can
be refrozen for future use.
3.7. Microscopy and Data Analysis
Combining synchronized phagocytosis with differential staining allows
precise quantification of total macrophage-associated bacteria as well as the
fraction of intracellular and extracellular
H. pylori
at each time point. For
each sample, analyze random fields of macrophages using immunofluores-
cence and phase-contrast microscopy. At least 50 infected macrophages should
be examined per sample and the number of green (FITC stained) and red
(rhodamine stained)
H. pylori
recorded. As all bacteria are stained green and
only uningested (extracellular)
H. pylori
are also stained red, the rate and extent
of phagocytosis at each time point can be calculated:
nogreen bacteria-no red bacteria
nogreen bacteria
%intracellular Hpylori
=
×
100
Other infection parameters can be measured, including infection efficiency
(fraction of infected cells), association index (total number of
H. pylori
per 100
macrophages), and phagocytic index (number of intracellular
H. pylori
per 100
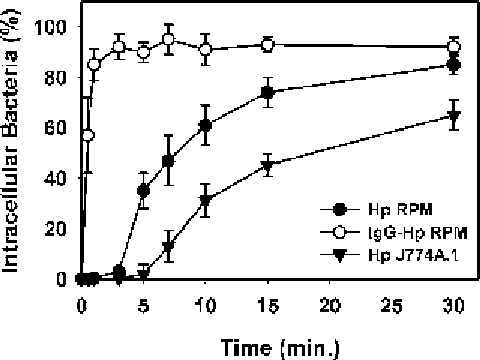
Fig. 2. Effect of cell type and opsonins on
Helicobacter pylori
phagocytosis.
H. pylori
strain 11637 (Hp) is ingested by resident peritoneal macrophages (RPM) after
a lag of several min. By contrast, uptake of IgG-opsonized Hp is rapid. Compared with
primary macrophages, infection of J774A.1 cells with Hp is less efficient. Data are the
mean
±
SEM of three independent experiments performed in triplicate.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search