Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Major-class
Minor-class
(1)
a avg d
a b c d
(2)
a
1
b
1
a
2
b
2
c
1
d
1
c
2
d
2
Major-
class
(3)
a
1
b
1
b
2
c
1
c
2
d
2
(4)
Minor-
class
a
1
b
1
b
2
c
1
c
2
d
2
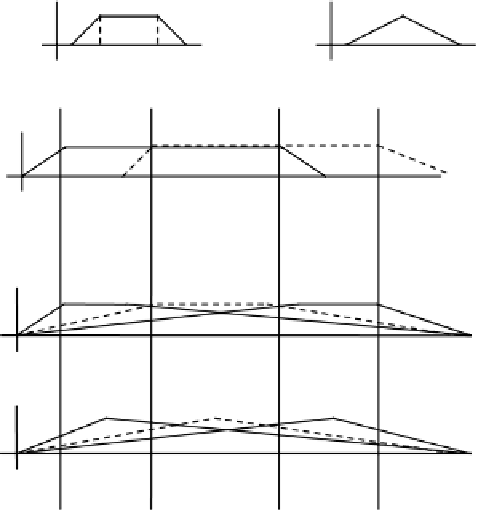
Fig. 2.5.
(1) Trapezoids for major-class membership functions and triangles for minor-class
membership functions. (2) Example of 2 overlapped trapezoids. (3) Three trapezoids will be
obtained from above if the membership functions would belong to the major-class and (4)
Three triangles if would belong to the minor-class. Both (3) and (4) have membership functions
with the minimum and the maximum in the limits of the variable.
The genetic algorithm uses the g-means metric (1), suggested by Kubat et al. 11, as
fitness value for imbalanced datasets.
+
−
g
=
acc
⋅
acc
(1)
The g-means is the most common measure used to evaluate results in imbalanced
datasets, where acc
+
is the accuracy classification on the positive instances, and acc
-
the accuracy on the negative ones.
The classification of the data, in a fuzzy logic system depends on the shape of the
membership functions of the input and output variables and the rules. The member-
ship functions of the input variables are obtained by the ReRecBF method, the rules
by means of this genetic algorithm and the output variable has to be defined from the
beginning. So, another important fact in the matching of the examples by the rule set
is the shape of the output trapezoids. We can choose between symmetric (they have
the same area and shape) or non-symmetric (they have different shapes and areas)
(Fig. 2.5), that is, both classes will have either the same importance or not.