Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
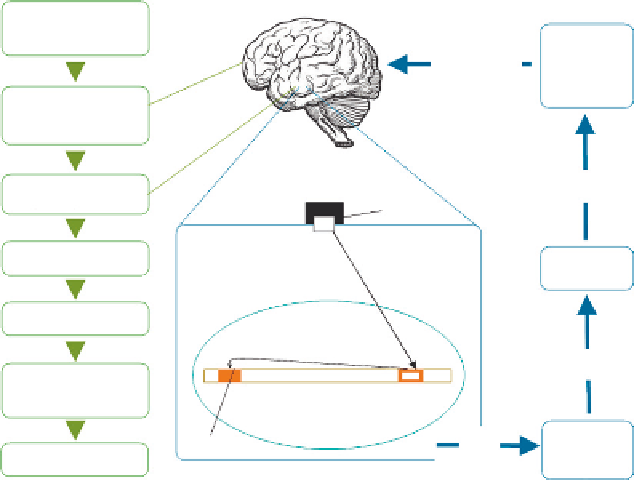
In a number of cases, the neurally induced DNA methylation is transmitted to
subsequent generations and leads to the inheritance of acquired characters in meta-
zoans. The illustrating example is the methylation of the
bdnf
gene. Licking and
grooming (LG) is a characteristically inherited behavior in rats. In this respect, there
are high-LG and low-LG rat mothers. Maternal high-LG behavior during the first
postnatal week is processed in the brain cortex of rat puppies where it activates a
signal cascade that leads to DNA demethylation and secretion of the neurotransmit-
ter serotonin in their hipocampal neurons. The binding of serotonin by its receptor
triggers a signal transduction pathway that leads to the activation of the gene
NGFIA
(nerve growth factor-inducible A) or
egfr
, inducing DNA demethylation and opening
of the chromatin, thus enabling expression of the glucocorticoid receptor (
GR
) gene
(
Figure 2.5
). As mothers, these puppies display the same high LG for their puppies.
However, when these puppies are reared by low-LG mothers they show their off-
spring the same low-LG behavior of their adopted mother rather than the high-LG
behavior of their biological mother. The reason for the transmission of the acquired
character (low-LG behavior) is that the processing of the insufficient maternal LG in
the brain cortex leads to DNA methylation and insufficient production of GR (
Szyf
et al., 2007
).
Parental care
Licking and grooming
GCs
Feedback
to the brain
Andrenal
gland
Processing of the
maternal tactile stimuli
in the cerebral cortex
ACTH
Secretion of serotonin
in hipocampal neurons
Serotonin
Serotonin
receptor
Blinding of serotonin
receptor
Pituitary
Secretion of NGFI-A
NGFI-A
CRH
DNA demethylation
and chromatin opening
GR gene
NGFI-A
gene
Nucleus
GR
GR gene
Hypothalamus
GR synthesis
Hipocampal neuron
Figure 2.5
The mechanism of transmission of the high-LG behavior in female rats. GR,
glucocorticoid receptor; CRH, corticotrophin-releasing hormone; ACTH, adrenocorticotropic
hormone; GC, glucocorticoid.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search