Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Anterior
lateral
mesoderm
Anterior
paraxial
mesoderm
Neural
tube
BMPs
Non-
cardiac
mesoderm
Wnts
Cardiac
mesoderm
Lateral
BMP-2
BMP-4
Noggin
Anterior
endoderm
signal
Notochord
Figure 3.29
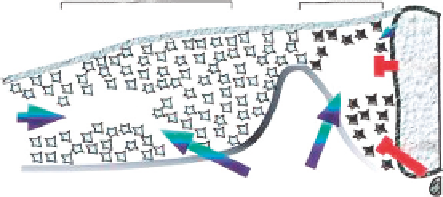
Heart formation is cued by a combination of positive and negative signals
from surrounding tissues. Although a signal or signals from the anterior endoderm work to
promote heart formation in concert with BMP signals in the anterior lateral mesoderm (blue
arrows), signals from the axial tissues (red) repress heart formation in the more dorsomedial
anterior paraxial mesoderm. Inhibitory signals that block heart formation in anterior paraxial
mesoderm include Wnt family members expressed in the dorsal neural tube (Wnt-1 and
Wnt-3a) and anti-BMPs expressed in the axial tissues (i.e., noggin in the notochord). We
suggest that the sum of these positive and negative signals determine the medial-lateral
borders of the heart-forming region.
Source
: From
Tzahor and Lassar (2001)
.
Along the signal cascade starting from Spemann's organizer and the local cardio-
genic induction, NCCs migrating to the heart Anlage from the cardial neural crest
are crucial to heart development (
Figure 3.30
). These NCCs originate in rhom-
bomeres 6, 7, and 8 of the hindbrain, where they are differentiated into various
mesenchymal cells and migrate to regulate formation of the heart outflow tract and
smooth muscles of the aortic arches (
Hutson and Kirby, 2007; Phillips et al., 1987
).
They induce the septation of the common outflow into separate aortic and pulmo-
nary arteries and influence ventral myocardial function and/or cardiomyocyte pro-
liferation (
Snider et al., 2007
). Recruitment of the NCCs in the development of the
cardiovascular system was crucial in the evolution of vertebrate cardiovascular sys-
tem as a “new” heart (
Fishman and Chien, 1997
). In contrast to other vertebrates,
in zebrafish, the cardiac neural crest invades the myocardium in all segments of the
heart, besides the outflow tract, atrium, atrioventricular junction, and ventricle (
Sato
and Yost, 2003
).
Removal of the cardiac neural crest in quail chick chimeras leads to anomalies
of all outflow and inflow heart structures in whose formation the NCC is involved
(
Miyagawa-Tomita et al., 1991
). Some recent evidence reducing the role of the car-
diac neural crest in the cardiovascular system of amphibians may result from the
smaller portion of the experimentally removed cardiac neural crest, but may also
reflect a loss in this structure's ability to migrate deep in the heart tube during the
Search WWH ::

Custom Search