Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Myoblast
Microtubule stabilization
Cell elongation, fusion
Myotube
LKB1 induced
Dynamic (tyrosinated) microtubule
Stable (detyrosinated) microtubule
Micro-tubule destabilization
and/or reorganization
Figure 3.10
Myoblasts contain a radial microtubule array that is a mixture of dynamic
microtubules and stabilized microtubules. Fully differentiated myotubes show a linear
microtubule array consisting of abundant detyrosinated/stable microtubules. Simple microtubule
stabilization blocks the formation of myotubes, and a transient decrease in microtubule
stabilization precedes cell elongation and fusion into myotubes. LKB1 plays a role in this
microtubule destabilization and/or reorganization, which accounts for its role in the differentiation
process.
Source
: From
Mian et al. (2012)
.
a substance that induces mechanical loosening of the actin cytoskeleton, leading to
its translocation to the opposite side of the sperm entry (presumptive anterior pole)
(
Mammoto and Ingber, 2010
).
The differential distribution of mRNAs determines the different fates of daugh-
ter cells of common origin. It is epigenetically determined, and the visible source of
epigenetic information necessary for the specific asymmetric distribution of mRNAs
seems to be the cell centrosome. The fact that different cells distribute mRNAs
differently in their daughter cells suggests that the widely held opinion that cen-
trosomes are informationally equivalent may be incorrect.
Epigenetic Determination of Early Development—The
Embryonic Genome Is Still Dormant
Epigenetic Determination of Cleavage Divisions
A number of maternal cytoplasmic factors are necessary to establish the dorsoventral
axis. In
Xenopus laevis
, since the first cleavage divisions, this axis is dertermined
by translating the maternal
Wnt
11 mRNA that is deposited into the vegetal pole of
the egg (
Ku and Melton, 1993
), and in the absence of
Wnt
11, these embryos do not
develop dorsal structures (
White and Heasman, 2008
). Wnt is primarily localized
in Spemann's organizer. As a dorsalizing maternal factor, it is involved in the pro-
cess of neurulation, and the neural tube becomes the main source of Wnt in early
development.
In zebrafish, another maternal transcript involved in specifying the dorsoventral
axis is the Nodal-related morphogen,
Squint
(
Sqt
), which localizes asymmetrically in
two blastomeres as early as the four-cell stage, thus determining the formation of the
dorsal embryonic structures. Early removal of cells containing
sqt
transcripts leads













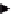








Search WWH ::

Custom Search