Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
a
=10
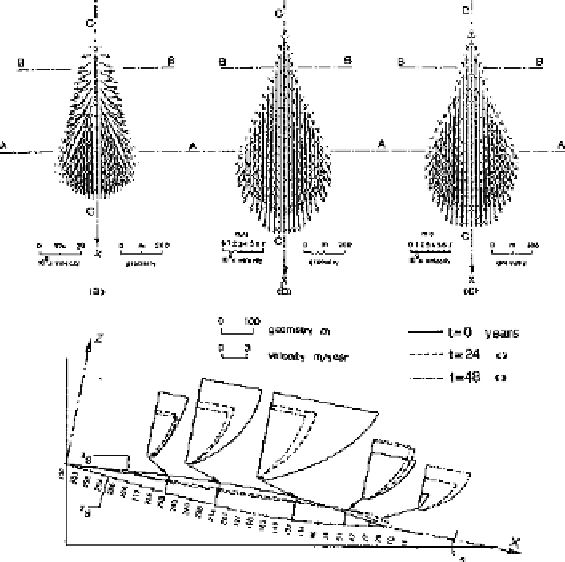
section C—C with velocity profiles
Figure 3.5.
Modeling of deformation as a function of time of a viscous three-dimensional
mass. Result of calculation [HUT 85]
These two material constants depend on the particle size and the mineralogy of
the materials in question, as well as the form of grains. They also depend on the
shear velocity, rate of deformation (in the case of a fragile material), drainage
conditions, compactness, even the temperature, degree of saturation (see section 3.4)
and chemical composition of the interstitial fluid. In addition, these parameters are
affected by the type of test.
Finally, expression [3.5] is sometimes expressed not as effective stress, but in
terms of total stress
σ
,
and the material constants are then usually designated by
c
u
for apparent cohesion and
φ
u
for apparent angle of internal friction.