Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
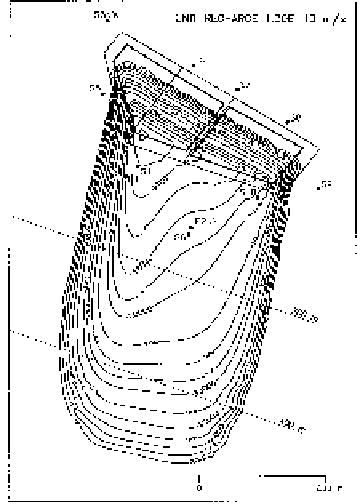
The scenario of dilution and attenuation factor obtained by a simplified model
that considers a constant concentration source of contaminant (i.e. infinite mass) and
does not take into account diffusive migration and sorption capacity of the bottom
liner but only advective migration is shown in Figure 16.8. Referring to these
results, the concentration phenols in the groundwater (c = 1.65 µg/l) does not
comply with the allowable limit given by the regulation (c = 0.5 µg/l).
Figure 16.8.
Distribution of dilution-attenuation-factor after 90 days
obtained with the MT3D model [MAN 97B]
The analysis has been repeated, improving the simulation model of barrier
performance and taking into account the finite amount of waste. The results are
shown in Figure 16.9, where it is possible to observe that a more accurate model can
highlight the fundamental role of the landfill liner, the leachate collection system
and the finite mass of pollutants. Therefore a correct evaluation of barrier
performance is fundamental in order to obtain a reliable risk analysis, referred to as
the subsoil safeguard against pollution.
Given the importance of a correct modeling of the mineral barrier for a reliable
risk analysis reinforces the importance of a reliable assessment of input parameters.
Due attention is not always given to the evaluation of these parameters, particularly