Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
−
Capping systems
have a lot of tasks to fulfill. Among them we can include: rise
of ground elevations in stable conditions; promotion of good surface drainage;
separate waste from animals and insects; separate waste from plant roots;
minimization of infiltration of water into waste; restriction of gas migration or
enhancement of gas recovery (in some sites); and other specific functions related to
post-closure developments on the landfill area [BOU 01].
16.5. Environmental impact evaluation (risk analysis)
Minimization of pollution due to leachate and gas migration into the subsoil or
atmosphere, respectively, is one of the major goals for the geoenvironmental
engineer; among other possible types of environmental impact. The evaluation of
landfill performance considering its location, the characteristics of the surrounding
environment, and referring in particular to the existence of a potential pollutant
target, is defined as “risk analysis”.
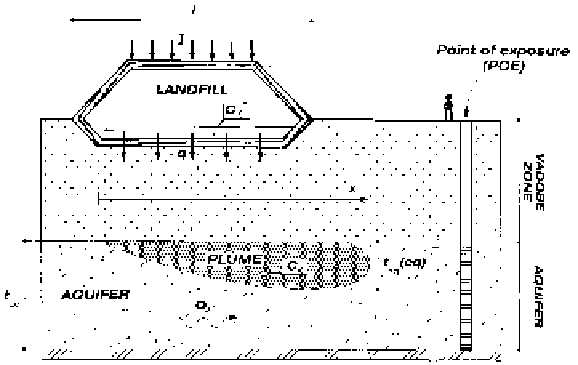
Figure 16.6 shows the conceptual scheme that is considered in the current type of
risk analysis for a polluted site or a landfill [CON 97, DIM 99]. The barrier and the
attenuation layers are generally located between the concentration
C
0
(initial
concentration of the contaminant) and
C
x
(concentration of the contaminant at
distance X), reported in the same figure.
I
represents infiltration through the cover or
surface of the containment,
l
the width of the containment,
q
the flow through the
base,
t
aq
thickness of the aquifer,
t
aq(eq)
thickness of the contaminant plume and
Q
o
is
the flow in the aquifer.
Figure 16.6.
Conceptual scheme for a contaminant impact evaluation
and risk analysis (modified from [DIM 99])