Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Soil surface
Soil surface
Surface du sol
Surface du sol
Saturation en
liquide
organique
dans la zone
non saturée
Saturation en
liquide
organique
dans la zone
non saturée
Saturation in
organic
liquid in the
vadose zone
Saturation in
organic
liquid in the
vadose zone
Zone
non saturée
Zone
non saturée
Vadose zone
Vadose zone
Frange
capillaire
Frange
capillaire
Capillary
fringe
Capillary
fringe
Liquide
Organique
LEGER
Liquide
Organique
LEGER
Light
NAPL
Light
NAPL
Water
table
Water
table
Nappe
phréatique
Nappe
phréatique
Saturated zone
Saturated zone
Zone
saturée
Zone
saturée
Dense
NAPL
Dense
NAPL
Flux
Flux
Flow
Flow
Liquide
Organique
DENSE
Liquide
Organique
DENSE
roche
roche
Rock
Rock
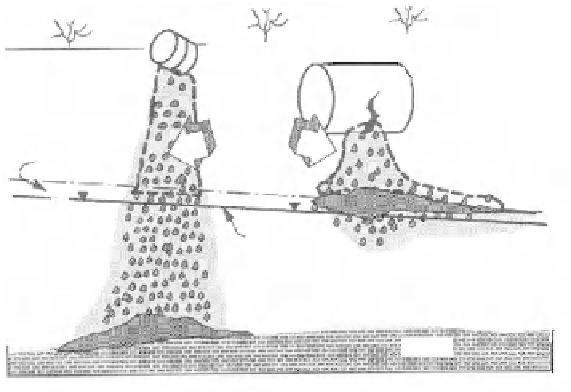
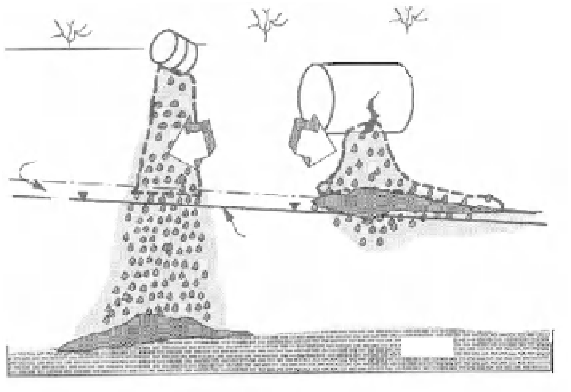
Figure 14.1.
Accidental infiltration of dense (left) and light
(right) NAPL in the vadose zone [WIL 90]
Crude oil is a complex combination of many organic molecules that can be
classified according to their molecular composition by the number of carbon atoms
in the molecular chain, together with their boiling temperature [ACA 00]:
− fuels (C
4
-C
8
, 80-150°C);
− kerosenes (C
11
-C
13
, 150-250°C);
− light gas oils (C
14
-C
18
, 250-325°C);
− heavy gas oils (C
19
-C
25
, 325-450°C) including lubricating oils from C
12
to C
20
;
− heavy oils (C
26
-C
40
, 450-500°C); and
− residues (C
>40
, > 500°C).
The main hydrocarbons in crude oil are paraffinic, naphtenic and aromatic
hydrocarbons (being either monocyclic or polycyclic hydrocarbons, according to the
number of benzene cycles in the molecule). In 1988, it was considered that 4-12%
of the 5-8 million underground stores containing either oil or chemical products in
North America were prone
to leaks and contaminating subsoils and water tables
[YON 91].
In Figure 14.1 we see that light NAPLs (the more frequent NAPLs, which
include fuels
and BTEX - benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene) infiltrate the
vadose zone due to gravity and capillary actions. They reach the water table and