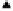Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
10
Double oedometer
Simple oedometer
8
6
4
2
0
0
5
10
15
20
25
Water content (%)
Figure 6.13
.
Collapse of soil 2.2 m at different initial water contents,
identified by simple and double oedometer methods
6.2.4.
Evaluation of various collapsibility criteria
As seen previously, the best way to assess the collapse susceptibility of soils is
based on the use of the oedometer, using either the simple or double oedometer
method. However, a simpler determination based on standard geotechnical
parameters would obviously be satisfactory and interesting, particularly for long
linear infrastructures. A number of authors have proposed such criteria that are now
examined on the samples at natural water content, and compared to oedometer
results.
As seen before, estimation according to Knight's criterion [KNI 63] leads the
2.2 m deep sample to the grading “slightly collapsible”.
1.7
1.6
4
3
1
1.5
1.4
2
Non collapsible
Collapsible
1.3
1.2
1.1
10
20
30
40
50
60
Figure 6.14.
Collapsibility of the four soils according to Gibbs and Bara [GIB 62]
w
L
(%)