Database Reference
In-Depth Information
Develop a decision tree data mining model in RapidMiner using a training data set.
Interpret the visual tree's nodes and leaves, and apply them to a scoring data set in order
to deploy the model.
Use different tree algorithms in order to increase the granularity of the tree's detail.
ORGANIZATIONAL UNDERSTANDING
Richard wants to be able to predict the timing of buying behaviors, but he also wants to
understand how his customers' behaviors on his company's web site indicate the timing of their
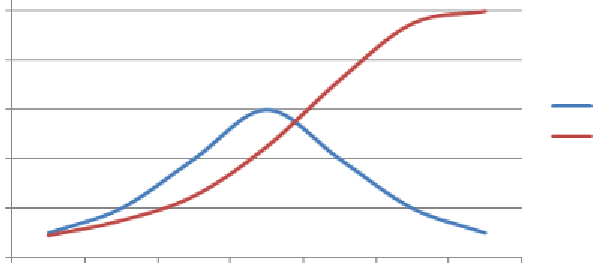
purchase of the new eReader. Richard has studied the classic diffusion theories that noted scholar
and sociologist Everett Rogers first published in the 1960s. Rogers surmised that the adoption of
a new technology or innovation tends to follow an 'S' shaped curve, with a smaller group of the
most enterprising and innovative customers adopting the technology first, followed by larger
groups of middle majority adopters, followed by smaller groups of late adopters (Figure 10-1).
Number of adopters by group
Cumulative number of adopters
over time
Figure 10-1. Everett Rogers' theory of adoption of new innovations.
Those at the front of the blue curve are the smaller group that are first to want and buy the
technology. Most of us, the masses, fall within the middle 70-80% of people who eventually
acquire the technology. The low end tail on the right side of the blue curve are the laggards, the
ones who eventually adopt. Consider how DVD players and cell phones have followed this curve.
Understanding Rogers' theory, Richard believes that he can categorize his company's customers
into one of four groups that will eventually buy the new eReader: Innovators, Early Adopters,
Early Majority or Late Majority. These groups track with Rogers' social adoption theories on the
diffusion of technological innovations, and also with Richard's informal observations about the
speed of adoption of his company's previous generation product. He hopes that by watching the