Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
15.2
Problem Definition and Notation
Let J be a set of customers and I a set of locations where facilities can be placed.
For each candidate location i
2
I,letf
i
be the cost of setting up a facility at i,and
for each arc .i;j/ with i;j
2
I
[
J,let`
ij
be its length or cost. The basic variant
of the LRP consists of choosing a set of locations from I and defining closed routes
starting and ending at one of these facilities such that each customer is visited by
exactly one of the routes, subject to side constraints. The goal is to minimize the total
cost, which typically includes the sum of facility set-up costs plus a traveling cost.
We also denote by G the underlying graph of an LRP instance formed by the set of
vertices V
D
I
[
J and the set of links E
D
E
IJ
[
E
I
,whereE
IJ
contains all links
connecting one facility with one customer, and E
J
contains all links connecting two
different customers. In what follows, both, directed and undirected formulations will
be presented. For ease of notation, E will be used indistinctly to denote the set of
(directed) arcs .i;j/ or the set of (undirected) edges
f
i;j
g
. For any set of nodes
S
V , E
S
will denote the set of links with both endpoints in S.
If a weight
w
j
is associated with each customer j
2
J, capacity constraints
can be considered by imposing a maximum weight Q delivered by a vehicle or
a maximum weight q
i
delivered from each facility i
2
I. From now on, Q will
be referred to as the vehicle capacity, and q
j
as the facility capacity and, for each
set of customers S
J,
w
.S/ will denote the total weight of customers in S:
w
.S/
D
P
j2S
w
j
. LRPs considering either type of constraint, or both of them, are
referred to as Capacitated LRPs (CLRPs). Additionally, many papers consider fixed
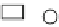
vehicle utilization costs, g, and a limited size fleet indexed in set K. Figure
15.1
depicts an LRP solution.
Further considerations and characteristics of the main elements of the problem
(number of facilities to locate, types of customers, size and characteristics of the
Fig. 15.1
Example of an LRP solution