Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
next
d
(
x
i
)=
x
i−d
mod
m
(1)
(
x
i
)
t
+
d
=
f
(
X
t
+
i−m
+
d
) f
m
−
d
≤
i<m
(2)
(
x
i
+
d
)
t
if
i<m
−
d
where
next
d
(
x
i
) is the cell connected to the output of
x
i
and
f
is the feedback
function. The Equation 1 corresponds to the transformation of the connections
between the memory cells. All the cells
x
i
of the original LFSR, such that
i
mod
d
=
k
, are gathered to form a sub-shift register, where 0
1. This is
the basic operation to transform a LFSR into a sub-sequences generator with a
multiple steps solution. The content of the last cell of the
k
-th sub-shift registers
corresponds to the
k
-th sub-sequence
S
d
. The Equation 2 corresponds to the
transformation of the feedback function. It must be noticed that the synthesis
requires to have only relations between the state of the register at time
t
+
d
and
t
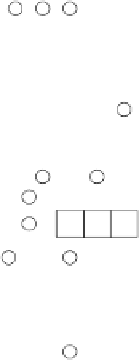
. The Figure 3 shows an example of such a synthesis for a Fibonacci setup
defined by the connection polynomial
q
(
x
)=
x
8
+
x
5
+
x
4
+
x
3
+ 1 with the
decimation factor
d
= 3. The transformation of a Galois setup is described by
the Equations 1 and 3:
≤
k
≤
d
−
⎧
⎨
(
x
0
)
t
+
d−m
+
i
⊕
m−
2
−i
a
i
+
k
(
x
0
)
t
+
d−k−
1
if
m
−
d
≤
i<m
k
=0
(
x
i
)
t
+
d
=
(3)
(
x
i
+
d
)
t
⊕
d−
1
⎩
k
=0
a
i
+
d−
1
−k
(
x
0
)
t
+
k
if
i<m
−
d
with
q
(
x
)=1+
a
0
x
+
a
1
x
2
+
+
a
m−
2
x
m−
1
+
x
m
. The Equation 3 does not
provide a direct relation between the state of the register at time
t
+
d
and
t
.
However, this equation can be easily derived to obtain more practical formulas
asshowninFigure4.
···
1-decimation
next
1
(
x
0
)=
x
7
1
(
x
i
)=
x
i
−
1
if
next
i
=0
(
x
7
)
t
+1
=(
x
3
)
t
⊕
(
x
4
)
t
⊕
(
x
5
)
t
⊕
(
x
0
)
t
x
7
x
6
x
5
x
4
x
3
x
2
x
1
x
0
S
(
x
i
)
t
+1
=(
x
i
+1
)
t
if
i
=7
3-decimation
3
(
x
0
)=
x
5
next
next
3
(
x
1
)=
x
6
x
6
x
3
x
0
S
3
3
(
x
2
)=
x
7
next
next
3
(
x
i
)=
x
i
−
3
if
i>
2
(
x
5
)
t
+3
=(
x
3
)
t
⊕
(
x
4
)
t
⊕
(
x
5
)
t
⊕
(
x
0
)
t
(
x
6
)
t
+3
=(
x
4
)
t
⊕
(
x
5
)
t
⊕
(
x
6
)
t
⊕
(
x
1
)
t
x
7
x
4
x
1
S
3
(
x
7
)
t
+3
=(
x
5
)
t
⊕
(
x
6
)
t
⊕
(
x
7
)
t
⊕
(
x
2
)
t
(
x
i
)
t
+3
=(
x
i
+3
)
t
if
i<
5
f
(
X
t
)
f
(
X
t
+1
)
f
(
X
t
+2
)
x
5
x
2
S
3
Fig. 3.
Multiple steps generator for a Fibonacci LFSR