Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
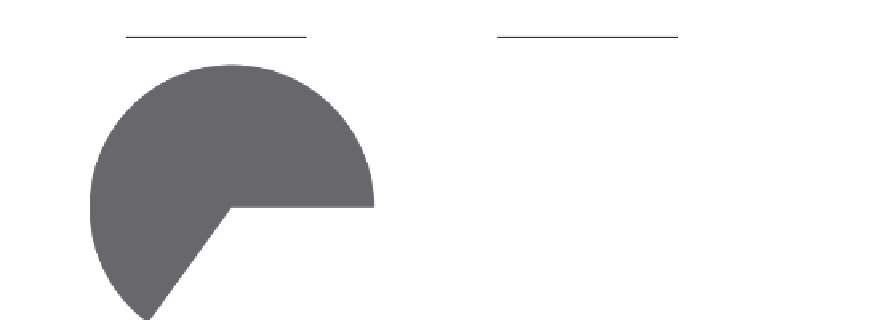
Hypothetical sample 1
Total periostin = 100 ng/ml
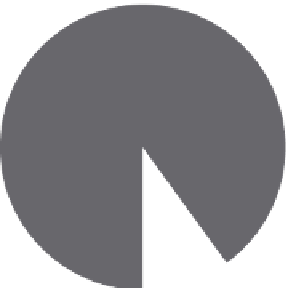
Hypothetical sample 2
Total periostin = 100 ng/ml
isoforms 2/4/5
65%
isoforms 2/4/5
90%
isoform 1
25%
Monoclonal capture reagent:
recognizes all isoforms equally
Polyclonal capture reagent:
affected by differences in isoform mixture
?
exons
1-16
17
18
19-23
1
3
2/4/5
Monoclonal
assay
Polyclonal
assay
FIGURE 4.3
Potential differences between monoclonal and polyclonal periostin immunoassays. The C-terminal
portion of periostin protein is subject to alternative splicing in exons 17-23 (lower right). Two hypothetical samples
with identical total periostin levels but with differing isoform composition (top) will yield similar results with a
monoclonal antibody-based assay that recognizes epitopes conserved in all splice variants but could yield differ-
ent results using a polyclonal antibody-based assay that contains a mixture of antibodies, some of which recognize
epitopes unique to certain splice variants.
Using the intensive airway sampling in BOBCAT to define phenotypes according to the
degree of sputum and/or tissue eosinophilia, we evaluated the relationships between air-
way eosinophilia and FeNO, blood eosinophils, and serum periostin (using the mAb-based
prototype periostin ELISA described above). Consistent with previous reports, we found
that measures of sputum and tissue eosinophils were only weakly positively correlated.
While some patients had elevations of either sputum or tissue eosinophils, others had ele-
vated eosinophils in neither or both compartments. Using either discrete classifiers with
pre-specified cutoff values for sputum and tissue eosinophils or continuous measures, we













































Search WWH ::

Custom Search