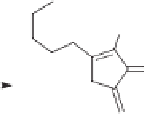
Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
4equivMeOH
Et
3
N1.5equiv
Cl
2
Pd (PPh
3
)
2
5mol%
CO 40 atm
100 °C, 24 h
O
a)
I
90% yield
ACN-benzene
19
20
MeO
2
C
Et
3
N1.5equiv
Pd(PPh
3
)
4
1 equiv
CO 40
160 °C, 24 h
TMS
TMS
atm
56% yield
O
b)
I
22
THF
21
Scheme 10.7
Palladium catalyzed [4
+
1] cyclocarbonylation.
The same research group described a similar reaction with 2-iodophenyl derivatives that
led to the synthesis of indenones (Scheme 10.8).
19
4 equiv MeOH
Et
3
N1.5equiv
Cl
2
Pd(PPh
3
)
2
5mol%
CO 40 atm
100 °C, 24 h
O
I
CO
2
Me
DMF
24
23a
Scheme 10.8
Synthesis of indenones via a Pd-catalyzed [4
+
1] cyclocarbonylation.
In 2003, Larock and co-workers reported the use of dienyl triflates, bromides and iodides
for the synthesis of cyclopentenones via a palladium-catalyzed reaction.
20
The reaction
proceeded optimally with the use of 10mol% of Pd(OAc)
2
, 2 equiv. of pyridine, 1 equiv.
of n-Bu
4
NCl, 1 atm. of CO, a reaction temperature of 100
◦
C and DMF as a solvent. This
methodology is particularly efficient for substrates that contain a terminal olefin, such as
23
. The reaction renders the final compounds in excellent yields as shown in Scheme 10.9.
Moreover, it appears that the nature of X (bromine, iodine or triflate) has little influence on
the outcome of the reaction.
Pd(OAc)
2
10 mol%
pyridine 2 equiv.
n
-Bu
4
NCl 1 equiv
1atmCO
O
X
X=OTf 95% yield
X=Br 87% yield
X=I 86% yield
DMF, 100 °C
25
23a-c
Scheme 10.9
Palladium catalyzed [4
+
1] cyclocarbonylation reported by Larock.