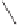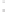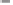Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Tab l e 6 . 5
Ligand exchange reaction of
t
-Bu-PNSO ligands.
X
X
Ph
P
Ph
N
N
CO
CO
Ph
O
O
OC
S
P
P
CO
S
t
-Bu-PNSO
Co
Co
OC
CO
OC
CO
CO
OC
Co
Co
Co
Co
Toluene,
Δ
OC
CO
OC
CO
R
R
R
1
37
37'
SM
∗
R
Ligand
X
Conditions
Product
Yield
d.r.
1i
TMS
35a
Bn
70
◦
C, 16h
37ia
78%
12:1
1i
TMS
35b
p
-MeO-Bn
65
◦
C, 24h
37ib
75%
12:1
1i
TMS
35c
p
-F-Bn
65
◦
C, 40h
37ic
99%
10:1
1c
CMe
2
OH
35a
Bn
65
◦
C, 16h
37ca
95%
7:1
1h
Ph
35a
Bn
65
◦
C, 5h
37ha
81%
8:1
1n
CH
2
OTBDPS
35a
Bn
65
◦
C, 6h
37na
85%
10:1
∗
Starting material
ligand (
35a
) provided excellent results for most substrates; however, in some cases, the
p
-methyoxybenzyl analog (
35b
) showed higher selectivity.
Although the
p
-Tol-PNSO ligands are not as selective or efficient as the
t
-Bu ligands
in PKRs of terminal alkynes, they have proven useful in the cyclization of symmetrically
substituted alkynes.
43
Internally symmetric alkynes are challenging substrates: firstly, they
are intrinsically less reactive than terminal alkynes; and secondly to achieve high selec-
tivity with them, coordination of the olefin to a single cobalt center is not sufficient—the
Tab l e 6 . 6
Ligand exchange reaction of
p-
Tol-PNSO ligands.
X
X
p-Tol
O
p-Tol
O
Ph
P
Ph
N
N
CO
CO
Ph
OC
S
P
P
S
CO
p-Tol-PNSO
Co
Co
OC
CO
OC
CO
CO
OC
Co
Co
Co
Co
Toluene,
Δ
OC
CO
OC
CO
R
R
R
1
38
38'
SM
∗
R
Ligand
X
Conditions
Product
Yield (%) d.r.
65
◦
C,2h
38ia
1i
TMS
36a
Bn
88
1:1
65
◦
C,2h
38ib
1i
TMS
36b
i
-Bu
62
2:1
65
◦
C,7h
38ic
1i
TMS
36c
i
-Pr
80
3:1
1c
CMe
2
OH
36b
i
-Bu
65
◦
C,2h
38cb
86
1:1
1h
Ph
36b
i
-Bu
65
◦
C,2h
38hb
93
1:1
1c
CMe
2
OH
36c
i
-Pr
65
◦
C, 5.5 h
38cc
81
1.3:1
1h
Ph
36c
i
-Pr
65
◦
C,2h
38hc
80
1:1
∗
Starting material