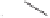Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
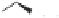
Bidentate (P,S) ligands with a chiral carbon skeleton were prepared in a few synthetic
steps from commercially available pulegone or camphorsulfonic acid. Importantly, total
diastereoselectivity was achieved in the key phosphinylation step to form the oxathianes
29
and
30
. The resulting ligands are best isolated as their borane adducts
36
(Scheme 6.21).
Me
Me
Me
O
O
O
R
R
Me
Me
S
P
Me
Me
S
Me
Me
BH
3
29
PuPHOS
·BH
3
R = Ph
CyPuPHOS
·BH
3
R = Cy
O
R
O
S
PR
R'
S
BH
3
30a
major
CamPHOS
MeCamPHOS
CyCamPHOS
·BH
3
R = Ph, R' = H
·BH
3
R = Ph, R' = Me
·BH
3
R = Cy, R' = H
·BH
3
R = t-Bu, R' = H
·BH
3
R = o-Tol, R' = H
s-BuLi, MeI
O
t
-BuCamPHOS
TolCamPHOS
SO
3
H
O
O
R
R
S
S
P
30b
minor
BH
3
epiCamPHOS
epiCyCamPHOS
·BH
3
R = Ph
·BH
3
R = Cy
Scheme 6.21
Bidentate (P,S) ligands derived from pulegone and camphorsulfonic acid.
The corresponding P,S bridged dicobalt-alkyne complexes
31
were conveniently pre-
pared by
in-situ
deprotection of the phosphine-borane ligands showed in Scheme 6.21 with
1,4-diazabicyclooctane (DABCO). Cobalt complexes
31
derived from terminal acetylenes
bearing bulky substituents (
1i
,
1j
and
1c
) afforded, after thermal equilibration, good diastere-
oselectivities (Table 6.2). Most importantly, the resulting diastereomers were easily sepa-
rated by chromatography or crystallization, and were bench stable. The methyl-substituted
derivative MeCamPHOS, which imposes a greater steric demand around the tetrahedral
cobalt-alkyne cluster, provided excellent diastereoselectivities (up to 20:1) for all three
complexes.
The diastereoselectivity of these ligands has been dramatically improved through use of
terminal propynamides as alkyne partners.
37
With these substrates, a non-classical hydrogen