Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
In 1999 and 2000 the group of Moyano reported that bidentate 2-(2-diphenylphos-
phinophenyl)oxazolines are superior chiral ligands for this transformation.
30
Their chelat-
ing coordination mode is the basis for the high bias achieved in the equilibration of the
diastereomeric complexes (85:15 using the phenyl derivative ligand
23a
and the complex
1h
; Scheme 6.16). Reactions of the
tert
-butyl derivative
23b
showcase the advantage of
chelation control: its higher steric demand provided the monocoordinated complexes
25
in nearly 1:1 diastereomeric mixture. The chelated complexes are much less prone to iso-
merization but, paradoxically, their PKRs provide only moderate enantiomeric excess (51
to 57% ee). More striking is the complete loss of enantiocontrol under
N
-oxide activa-
tion. Despite the low diastereomeric excesses obtained in the ligand exchange reaction, the
monocoordinated complexes
25
provide high levels of asymmetric induction, especially
under
N
-oxide activation. One could speculate that the free imino nitrogen provides some
form of anchimeric assistance in these reactions.
O
OC
CO
H
OC
CO
N
P
OC
CO
N
N
23a
Co
Co
Co
Co
Ph
+
OC
24
CO
P
P
Toluene
60 °C
H
Ph
Ph
OC
CO
24/24'
3h
(57% ee)
OC
CO
91% yield
dr 85:15
Co
Co
OC
CO
Ph
O
H
OC
CO
OC
CO
P N
1h
OC
CO
OC
CO
23b
Co
Co
Co
Co
Ph
+
25'
OC
P
P
CO
NMO
CH
2
Cl
2
, 0 °C
N
N
H
Ph
Ph
25/25'
3h
(97% ee)
O
O
dr 1:1
99% yield
N
N
Ph
t-Bu
PPh
2
PPh
2
23a
23b
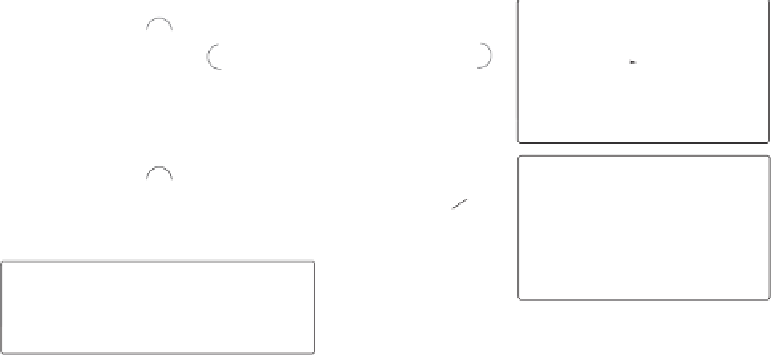
Scheme 6.16
(
P
,
N
) bidentate ligands that can function as either monodentate or chelating
ligands, thereby offering distinct diastereo- and enantio-selectivities.
Phosphoramidites are another type of chiral ligand used in intermolecular PKRs. BINOL-
derived phosphoramidites are highly modular compounds that have been used in numerous
asymmetric transformations. In a strategy devised by Gimbert et al., two of these ligands are
incorporated into the dicobalt-alkyne cluster, thereby obviating diastereomer separation
31
(Scheme 6.17). Although this strategy provides only moderate to low induction in stoichio-
metric PKRs with norbornene, it remains conceptually interesting. Firstly, it demonstrates
that in terms of reactivity, phosphoramidites are promising PKR ligands, as indicated by
the fact that coordination of related phosphines at both cobalt centers leads to a drastic
reduction in reactivity. Secondly, this strategy showcases a feasible approach for future cat-
alytic versions of the PKR, via intermediacy of a single diastereomer at the dicobalt-alkyne
complex stage within the catalytic cycle.
Attempts to extend the well-established BINAP chemistry to the intermolecular asym-
metric PKR have met little success. In a seminal contribution, Hiroi screened the same