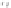Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
H
H
Me
2
CuLi, Et
2
O, 0 ºC
O
O
86%
O
O
Me
O
O
Me
3
Si
Me
3
Si
Ph
Ph
Ph
Ph
H
H
H
H
40b
(Major isomer)
p
-TsOH, acetone,
rt, 2 h
98%
H
H
p
-TsOH, acetone,
reflux, 56 h
41
O
O
O
57%
Me
Me
O
O
Ph
Ph
H
H
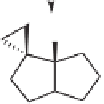
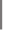
Scheme 5.34
Me
Me
Me
N
OMe
N
OMe
N
OMe
Co
2
(CO)
8,
hexane, rt;
Me
Me
Me
+
NMO, CH
2
Cl
2,
rt,
0.5 h;
SiO
2
purification
MeO
N
MeO
N
MeO
N
H
28%
28%
H
H
O
O
1) Allylation
2) Propargylation
Aq HCl, dioxane, rt, 5 h
Me
N
OMe
Me
NH
2
CO
2
Me
NH
2
CO
2
Me
O
O
MeO
N
H
H
42
43
(40%)
44
(51%)
Scheme 5.35
5.3 Asymmetric Intermolecular PKRs with the Aid of Chiral Auxiliaries
5.3.1 Chiral Alkoxyacetylenes
Stereochemical control in intermolecular PKRs, clearly more challenging than in the
intramolecular mode, was first addressed with encouraging results through the use of steri-
cally biased chiral alcohols as auxiliaries.
35
It could be rapidly established that the dicobalt
hexacarbonyl complexes of chiral alkoxyethynes
14
underwent a totally regioselective in-
termolecular PKR with norbornene (Table 5.5) and with cyclopentene (Table 5.6), under