Civil Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
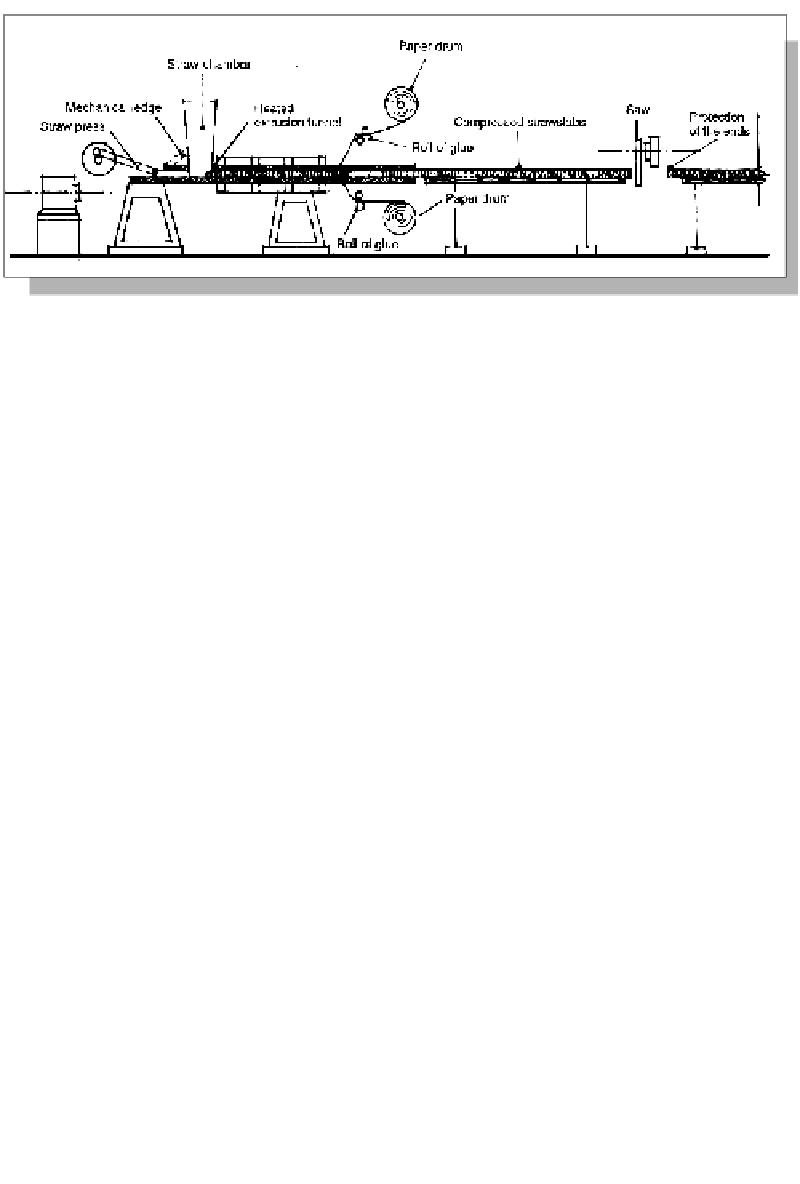
Figure 15.28: Production of strawboards. Source: Stramit
3.
The boards are put under pressure in a closed chamber at a temperature of 200°C.
4.
They are cooled.
5.
They are cut to size.
6.
The porous boards are coated with an adhesive and are then covered with a stiff
paper, preferably recycled, which gives them rigidity.
Boarding from domestic waste
Boards made of waste are still at an experimental stage. There have been experi-
ments with products to be used internally, for boarding under different finishes,
on walls and on floors. The use of this raw material is very interesting environ-
mentally speaking. It may contain contaminants such as plastic, which can affect
the indoor climate negatively. There is also a risk of emissions from binding
agents that may be used. There may even be a need to add fungicide to the
boards. But if these boards are not treated in any way, then they can probably be
recycled into the same sort of product again.
Manufacture of rubbish boards
The manufacture of these boards begins in the local authority rubbish tip and proceeds as
follows:
1.
The rubbish is crushed and ground. Iron is separated by electromagnets and heavy
articles are sieved away.
2.
The homogenized mass is dried at 148°C to a moisture content of 3-5 per cent.